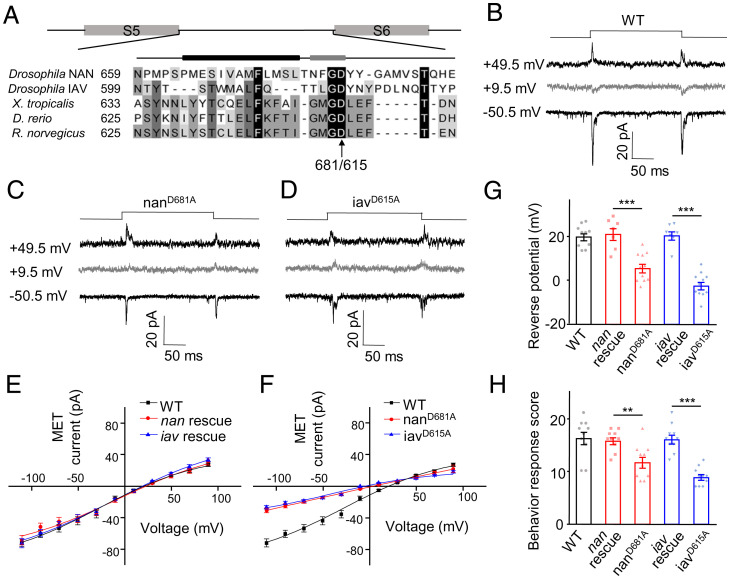
Fig. 5.
Point mutations of NAN and IAV in selective filter regions shifted the reversal potential of MET current. (A) Sequence alignment of the putative pore regions of NAN and IAV and their homologs. The arrow marks the negatively charged residue Asp mutated to Ala. The putative pore helix (black bar, Left) and selectivity filter (gray bar, Right) are indicted above the sequences. (B–D) Representative traces of current responses to 1-μm displacement in wild-type and two selectivity filter mutants (nanD681A and iavD615A). Lch1 neurons were recorded in extracellular Na+/intracellular Cs+-based solutions with TEA. (E) Average current–voltage relationship of MET currents recorded from wild-type, nan rescue, and iav rescue larvae. Lch1 neurons were recorded in Na+/Cs+-based solutions (mean ± SEM; n = 10, 7, and 7, respectively). (F) I–V relations of MET currents in lch1 neurons of nanD681A (n = 11) and iavD615A (n = 11). MET currents of the wild-type were used in each graph for comparison. Lch1 neurons were recorded in Na+/Cs+-based solutions. All error bars denote ± SEM. (G) The reversal potential of MET currents in lch1 neurons recorded from larvae with the indicated genotype (mean ± SEM; n = 10, 7, 11, 7, and 11). (H) Summary of behavioral response of transgenes encoding wild-type and mutant forms of nan and iav (n = 10 for each group). The sound stimulus was 500 Hz pure tone. The unpaired t test was used for comparison between two groups, and one-way ANOVA followed by Holm–Šidák post hoc analysis was used for comparison among multiple groups. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. Genotypes are as follows: nanD681A: Iav-Gal4, UAS-GFP/UAS-nanD681A-GFP; nan36a/nan36a. iavD615A: iav1/y; Iav-Gal4, UAS-GFP/+; UAS-iavD615A-GFP/+. nan rescue: Iav-Gal4, UAS-GFP/UAS-Nanchung-GFP; nan36a/nan36a. iav rescue: iav1/y; Iav-Gal4, UAS-GFP/+; UAS-Inactive-GFP/+. WT: Iav-Gal4/+; UAS-CD8-GFP/+.