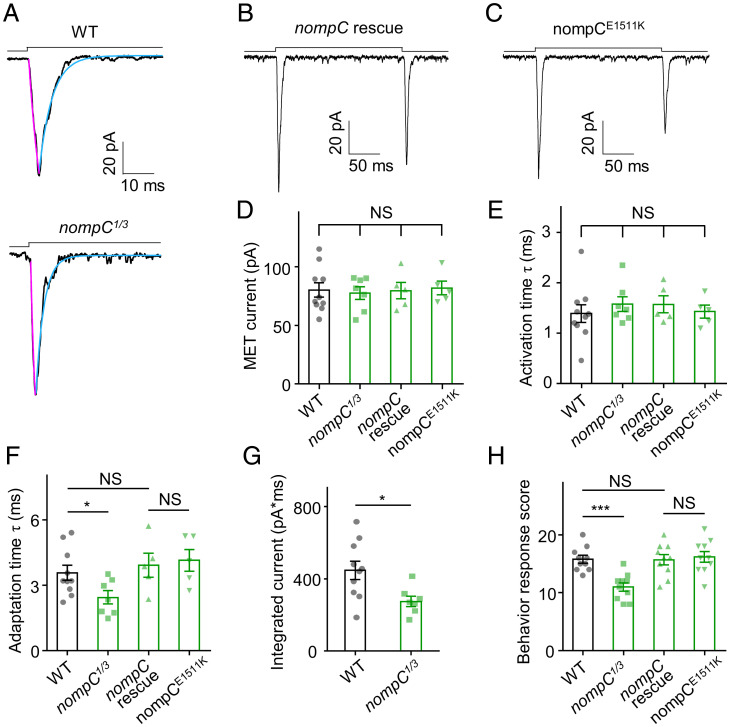
Fig. 7.
NompC regulates the adaptation time of MET currents in Cho neurons. (A) Representative traces of MET currents from wild-type and nompC1/3 null mutants. Cyan lines represent single exponential fits of the adaptation of MET currents; purple lines represent single exponential fits of the activation of MET currents. (B and C) Representative traces of MET currents from wild-type nompC rescue and nompCE1511K mutant larvae. (D) Summary of MET current amplitudes (absolute value) of wild-type, nompC1/3, nompC rescue, and nompCE1511K (mean ± SEM, n = 10, 7, 5, and 5). (E) Activation time constants of MET current in wild-type, nompC1/3, nompC rescue, and nompCE1511K (mean ± SEM, n = 10, 7, 5, and 5; NS, not statistically significant). (F) Adaptation time constants of MET current in nompC1/3 were smaller than those in wild-type, nompC rescue, and nompCE1511K (mean ± SEM, n = 10, 7, 5, and 5). For A–F, lch1 neurons were clamped at −60 mV (holding potential) in Na+/K+-based solutions. (G) Statistical analysis of integrated MET currents of wild-type and nompC1/3 (mean ± SEM; n = 10 and 7). (H) Summary of behavioral response of wild-type, nompC1/3, nompC rescue, and nompCE1511K (n = 10 for each group). The sound stimulus was 500 Hz pure tone. The two-tailed unpaired t test was used for comparison between two groups, and one-way ANOVA followed by Holm–Šidák post hoc analysis was used for comparison among multiple groups. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001; NS, not statistically significant. Genotypes are as follows: WT: Iav-Gal4/+; UAS-CD8-GFP/+. nompC1/3: nompC1/nompC3; Iav-Gal4/UAS-CD8-GFP. nompC rescue: nompC1/nompC3; Iav-Gal4, UAS-CD8-GFP/UAS-nompC-GFP. nompCE1511K: nompC1/nompC3; Iav-Gal4, UAS-CD8-GFP/UAS-nompC-E1511K-GFP.