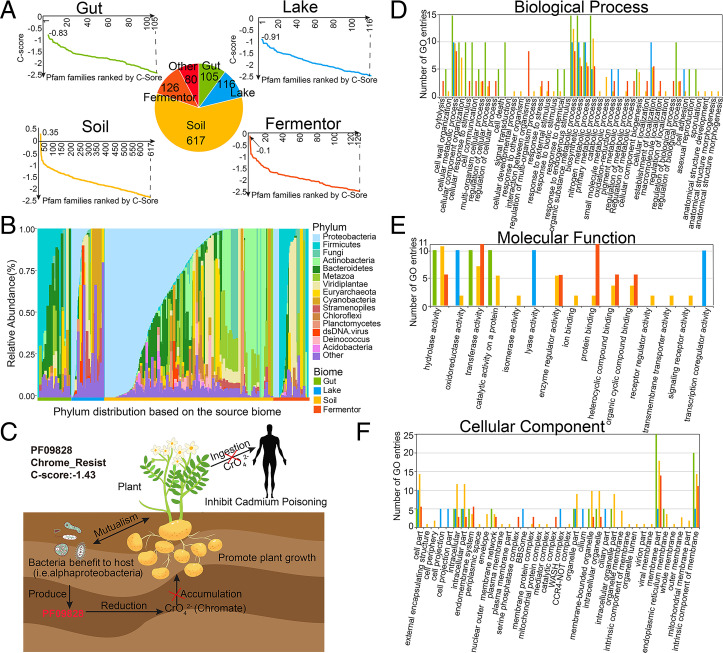
Fig. 3.
The taxonomic and functional properties of the Pfam families foldable by C-I-TASSER. (A) C-score distribution for Pfam families after replenishing by metagenome sequences. The vertical axis represents the C-score. For each panel, horizontal axis represents the Pfam families (31). (B) The relative abundance of species distribution for Pfam families which were foldable by C-I-TASSER. The species distribution is divided into four biomes and labeled with different colors. Calculated by the average count among all samples, the top 10 phyla are illustrated and ranked. “Other” represents the combination of the rest of the phyla. (C) Proteins in PF09828 are involved in the reduction of chromate accumulation and are essential for chromate resistance. Bacteria that hosts in plant produce the proteins identified as PF09828 to reduce the accumulation of chromate, resulting in the fast growth of the plant and preventing the transmission of cadmium to humans through the food chain leads to cadmium poisoning. For all the Pfam families which were foldable by C-I-TASSER, after aligning the Pfam species to the Interpro database, their protein functions were annotated by GO annotations and classified by three top annotations: Biological Process (D), Molecular Function (E), and Cellular Component (F).