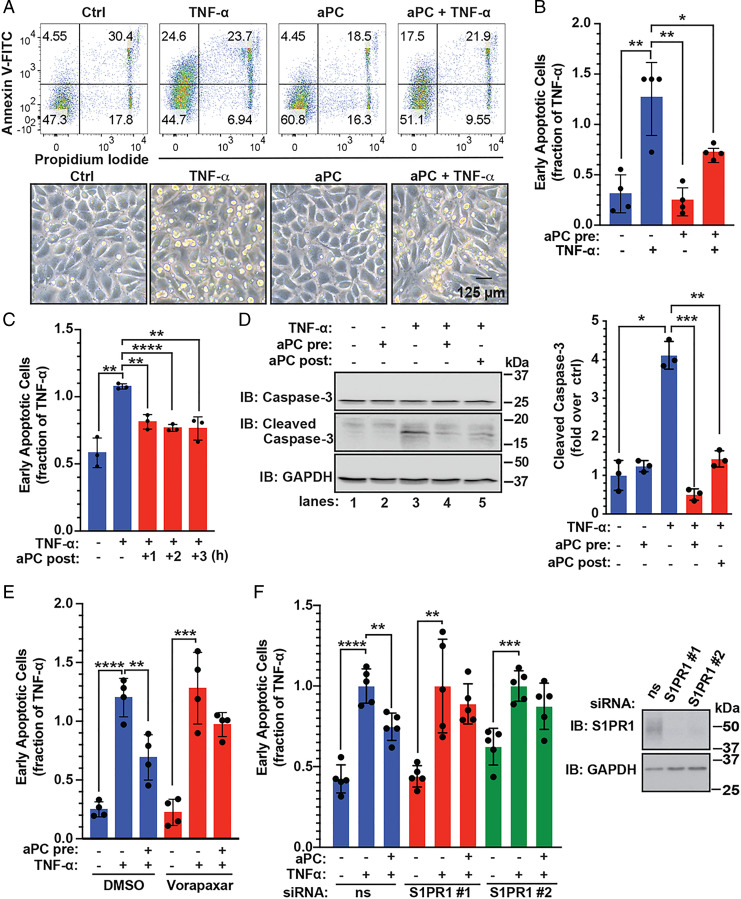
Fig. 2.
PAR1 and S1PR1 mediate aPC anti-apoptotic activity in endothelial cells. (A) EA.hy926 cells were pretreated with 20 nM aPC for 4 h and then treated with 10 ng/mL TNF-α for 20 h or left untreated, control (Ctrl). (Top) Cell death was determined by flow cytometry using Annexin V-FITC and PI. (Bottom) Phase–contrast images of endothelial cells. (Scale bar, 125 µM.) (B, Top Right) The data (mean ± SD, n = 4) of the early apoptotic response were analyzed by t test. (C) EA.hy926 cells were treated with TNF-α for 20 h and then aPC was added for 1, 2, or 3 h. The data (mean ± SD, n = 3) were analyzed by t test. (D) EA.hy926 cells were pretreated with aPC for 3 h and followed by TNF-α for 20 h, or aPC was added 3 h post–TNF-α. Cleaved caspase-3 and GAPDH were detected by immunoblotting (IB). Data (mean ± SD, n = 3) was analyzed by t test. (E) EA.hy926 cells were pretreated with 10 µM vorapaxar for 1 h, stimulated with aPC for 4 h, then treated with TNF-α for 20 h, and apoptosis determined. Data (mean ± SD, n = 4) were analyzed by two-way ANOVA. (F) EA.hy926 cells transfected with nonspecific (ns) or two different, S1PR1-specific siRNAs were stimulated with aPC for 4 h and treated with TNF-α for 20 h. S1PR1 and GAPDH were detected by immunoblotting. Data (mean ± SD, n = 5) were analyzed by two-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; and ****P < 0.0001.