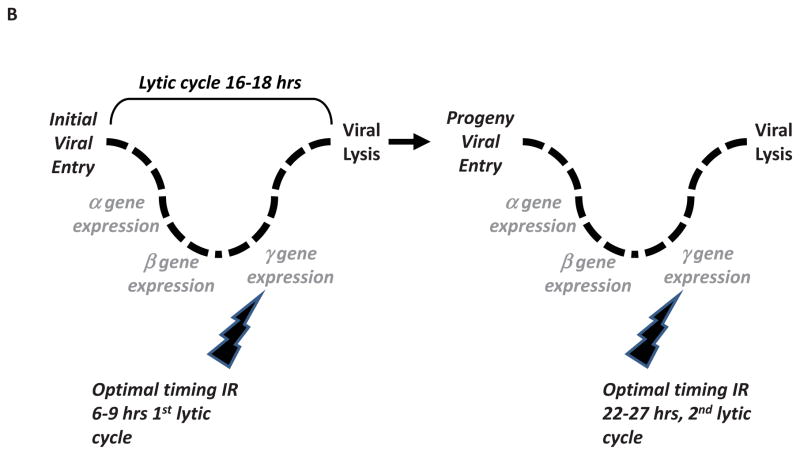
Figure 4.
Mechanistic Model of the Interaction of Radiation and Oncolytic HSV-1. 4A: The interaction of IR during a single HSV-1 replicative cycle. Following receptor mediated internalization of HSV-1, a temporal cascade of HSV-1 gene expression occurs. Initial α gene expression is followed by β genes (function to replicate viral DNA), and finally γ genes (involved in assembly of progeny virus). Ionizing radiation has been shown to enhance replication of HSV-1 by multiple mechanisms. As depicted, IR delivered at different times in relation to the viral replicative cycle can enhance the oncolytic ability of viruses. 4B: Clinically incorporating radiotherapy with oncolytic HSV-1. As oncolytic viruses replicate and spread within tumor, radiotherapy could be optimally delivered so as to coincide with late viral gene expression (i.e. 6–9 hrs after viral entry) in later viral replicative life cycles. This interaction may be clinically incorporated into hypofractionated radiotherapy.