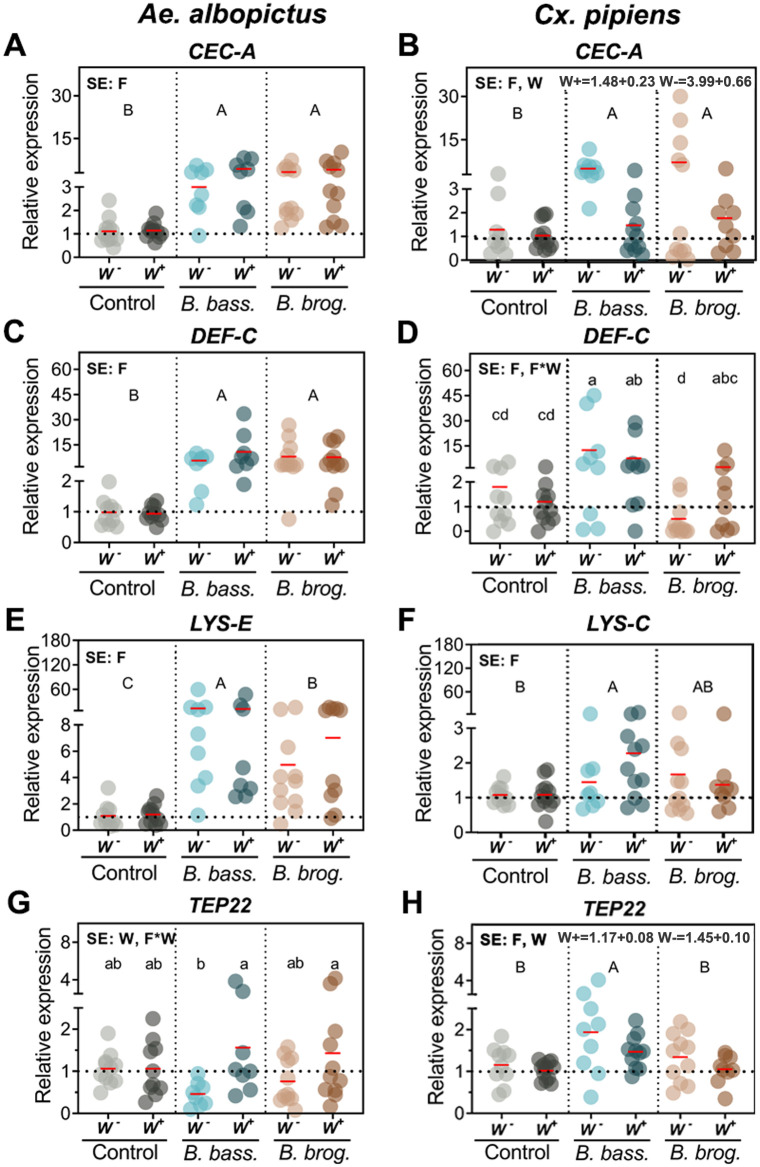
Fig 3. Gene expression of anti-microbial effectors as a result of natural Wolbachia and fungal entomopathogenic infections.
Significant effects (SE) indicate whether the independent factors: Fungal entomopathogen (F), Wolbachia presence (W) or their interaction (F*W) were statistically significant. Lowercase letters indicate interactive effects (F*W), uppercase letters refer to fungal effects and any Wolbachia effect is represented by their mean and standard deviation on the upper right corner of the graph. The red horizontal line indicates LS-means from eight to eleven biological replicates per treatment, originating from at least three independent experiments. Groups sharing the same letter are not significantly different at p<0.05 based on differences of least-squares means. W-, Wolbachia-free; W+, Wolbachia-infected; B. bass., B. bassiana; B. brog., B. brongniartii. CecA, Cecropin A; Def-C, Defensin C; Lys-E, Lysozyme E; Lys-C, Lysozyme C; TEP22, Thioester-containing protein 22. See Table 1 for complete statistics from the Two-Way ANOVA.