Figure 8. Intranasal administration of club cocktail improves therapeutic efficacy of α-PD-1 antibody in vivo.
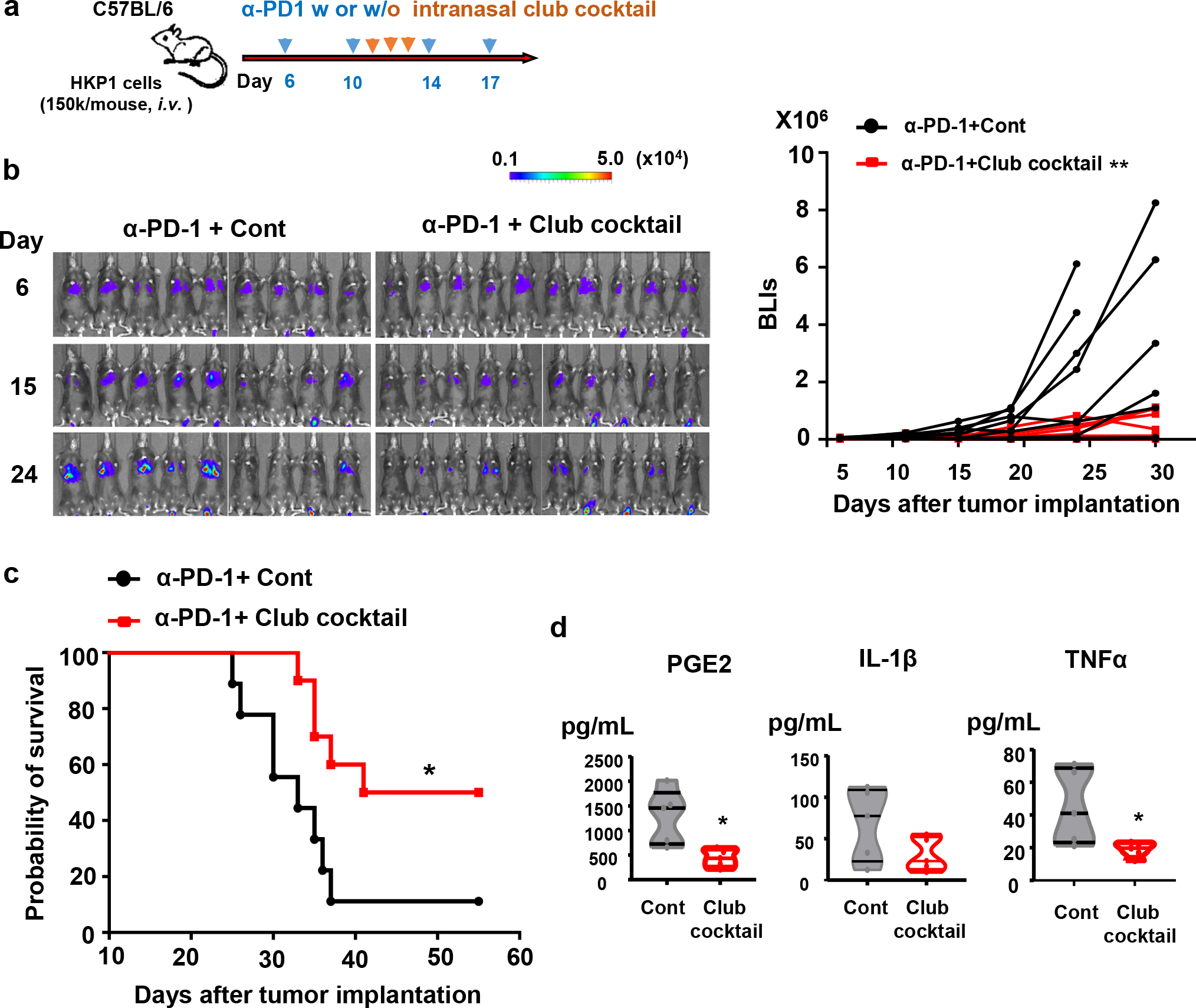
a. Schematic depicting treatment strategies. HKP1-bearing mice were treated with α-PD1 antibody (0.25mg/mouse, i.p.) at day 6, 10, 14, and 17. Mice also intranasally received a mock control or the club cocktail at day 11, 12 and 13, 20ng/protein/mouse.
b, Reduced tumor burden in mice receiving club cocktail. Left : Bioluminescent images (BLIs) of HKP1 mice treated with α-PD-1+Cont (n=9 mice) or α-PD-1+ Club Cocktail (n=10 mice). Right: tumor growth curves of HKP1 mice described in the left panel, **P = 0.0053, two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s post-hoc test. This experiment was repeated, and similar trends were observed.
c, Kaplan-Meier survival curves of HKP1 mice receiving α-PD-1 together with a mock control (n=9 mice) or the club cocktail (n=10 mice), *P = 0.0175, Two-tailed logrank test with Bonferroni method.
d. ELISA of inflammatory factors (IL-1β, PGE2, and TNFα) in the BALF. BALF were collected at Day 14 from mice intranasally treated with the mock control or club cocktail at day 11, 12, and 13, 20ng/protein/mouse. n=5 BALF samples from 5 mice, unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test. PGE2: *P=0.0118; IL-1β: P=0.1218; TNFα: *P=0.037.
