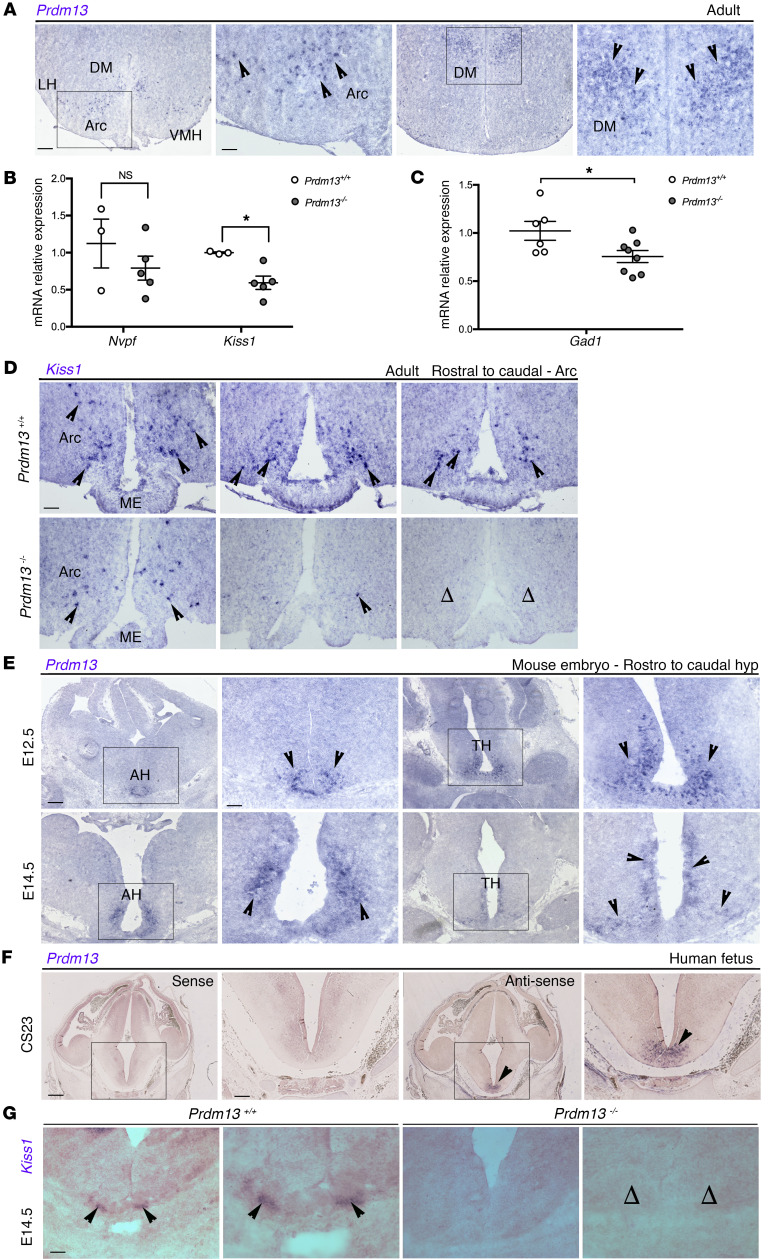
Figure 3. Prdm13 loss affects Kiss1 expression and Kiss1 neuron development.
(A) In situ hybridization on coronal adult WT male mice brain sections to detect Prdm13 expression in the Arc and DM nuclei of the hypothalamus, indicated by black arrowheads. (B) qRT-PCR analysis for Npvf and Kiss1 transcripts in the hypothalamus of Prdm13+/+ and Prdm13–/– male mice. ΔΔCq was calculated relative to control samples using Cq threshold values normalized to the housekeeping gene Gapdh. Note the significant decrease of Kiss1 levels in mutants. *P < 0.05, 2-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. (C) qRT-PCR analysis for Gad1 transcripts in the hypothalamus of Prdm13+/+ and Prdm13–/– from both sexes. ΔΔCq was calculated relative to control samples using Cq threshold values that were normalized to the housekeeping gene Gapdh. Note the significant decrease of Gad1 levels in mutants. *P < 0.05, 2-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. (D) In situ hybridization on coronal sections from the Arc nucleus level from Prdm13+/+ and Prdm13–/– male mice, detecting Kiss1 transcripts. Note the reduction in Kiss1 expression in the mutants compared with WT controls, where open arrowheads indicate complete absence of expression. (E and F) In situ hybridization on coronal sections detecting Prdm13/PRDM13 expression in the developing mouse hypothalamus at E12.5 and E14.5 (E) and developing human hypothalamus at CS23 (F). mRNA transcripts are indicated by the arrowheads. The sense probe showed negative staining (first 2 images from the left). (G) In situ hybridization on coronal sections from E14.5 mouse embryo to detect Kiss1 expression in Prdm13+/+ and Prdm13–/–. Black arrowheads indicate examples of Kiss1-expressing cells; note the absence of Kiss1 neurons in mutants (open arrowheads). Areas within marked rectangles are shown in high magnification in adjacent images. Scale bars: 500 μm (A, E, and F, low magnification), 250 μm (A, E, and F, high magnification; D and G). LH, lateral hypothalamus; VMH, ventromedial hypothalamus; AH, anterior hypothalamus; TH, tuberal hypothalamus.