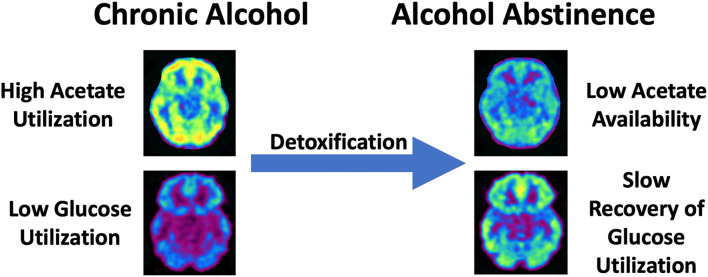
Figure 2.
Schematic overview of the shift from high acetate utlization to low brain acetate avaliability with slow recovery of brain glucose metabolism in chronic AUD during detoxification. This shift is hypothesized to produce a central energy deficit that could contribute to alcohol withdrawal symptoms and associated neurotoxicity.