Figure 2:
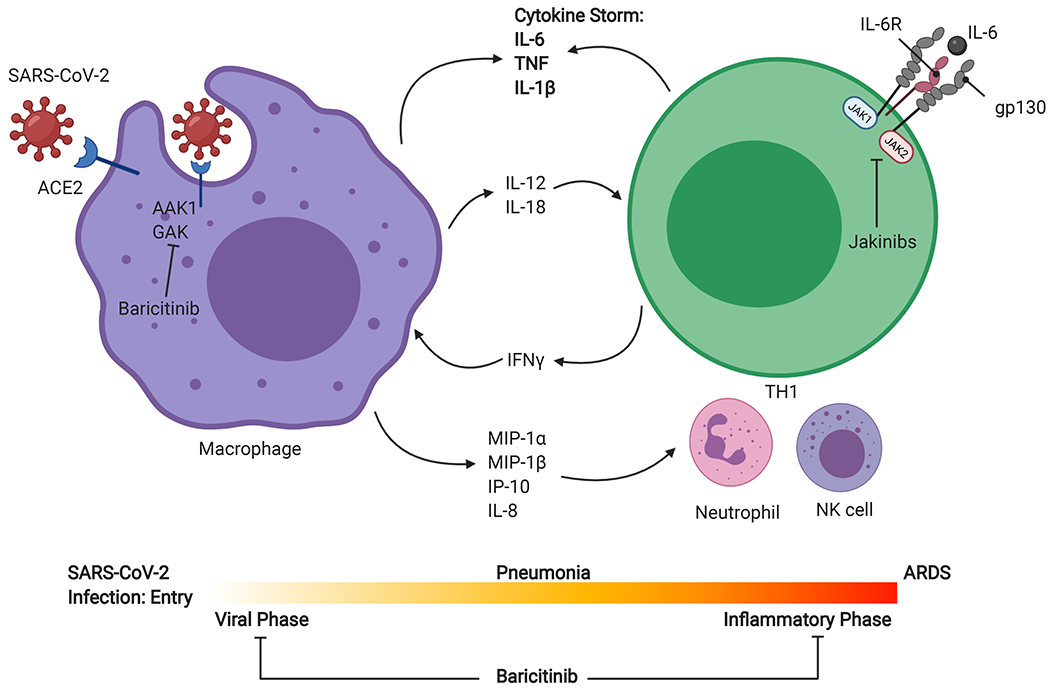
SARS-CoV-2 entry is mediated by ACE2 (Angiotensin converting enzyme 2), a receptor widely expressed in the lungs, heart, vasculature, kidneys, and gastrointestinal tract. Primary site of infection is alveolar epithelial cells in the lungs, and rapid replication of virus can lead to a hyperimmune response. Macrophage activation and chemokine release for neutrophil, TH1, and NK cell recruitment can lead to a massive cytokine release responsible for the clinical evolution to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Jakinibs such as baricitinib can potentially block viral entry by inhibiting numb-associated kinase family (NAK) proteins AAK1 and cyclin G-associated kinase (GAK). During the inflammatory phase, many of the cytokines elevated in Covid-19 (IL-6, IL-12, and IFNγ) signal via JAKs, and therefore, jakinibs are being considered as potential therapeutics in severe SARS-CoV-2. JAK, Janus kinase; TYK, tyrosine kinase; IL, interleukin; MIP, macrophage inflammatory protein; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; IP, interferon γ-induced protein. Created with BioRender.com
