Figure 3:
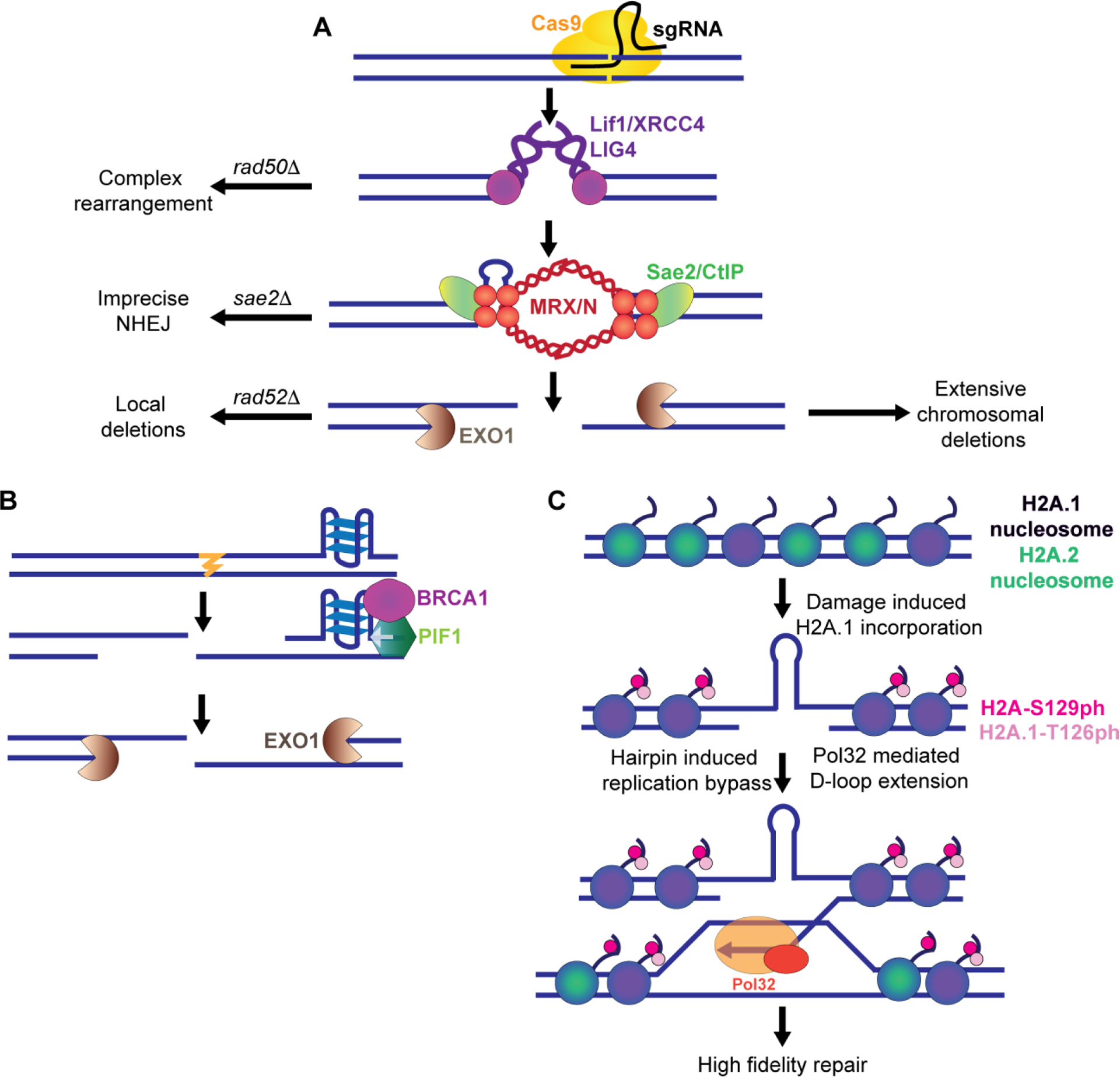
Navigation of resection and repair synthesis through microsatellites. A. At a CrispR/Cas9 break targeting the CTG repeat, repair results in various chromosomal changes. In NHEJ defective rad50Δ mutants, complex rearrangements can be found. In the absence of Sae2, which processes hairpin capped ends, repair occurs via imprecise end-joining. After long range resection by Exo1, repair can result in SSA mediated long range deletions while loss of RAD52 results in smaller local deletions. B. Resection can be impeded by DNA secondary structures. Pif1, which unwinds G4 structures, interacts with BRCA1 to unwind secondary structures that impede long range resection. C. Replication of bypassed DNA hairpins or DNA damage at an expanded CAG repeat tract results in incorporation of copy 1 of histone H2A (H2A.1) which can be phosphorylated at a threonine 126 on the histone tail. The incorporation of histone H2A.1 and phosphorylation of T126 promote efficient D-loop extension during sister chromatid recombination or other D-loop mediated repair, resulting in high fidelity repair and preventing repeat expansions.
