Figure 2. Effects and functions of EVs in the central nervous system.
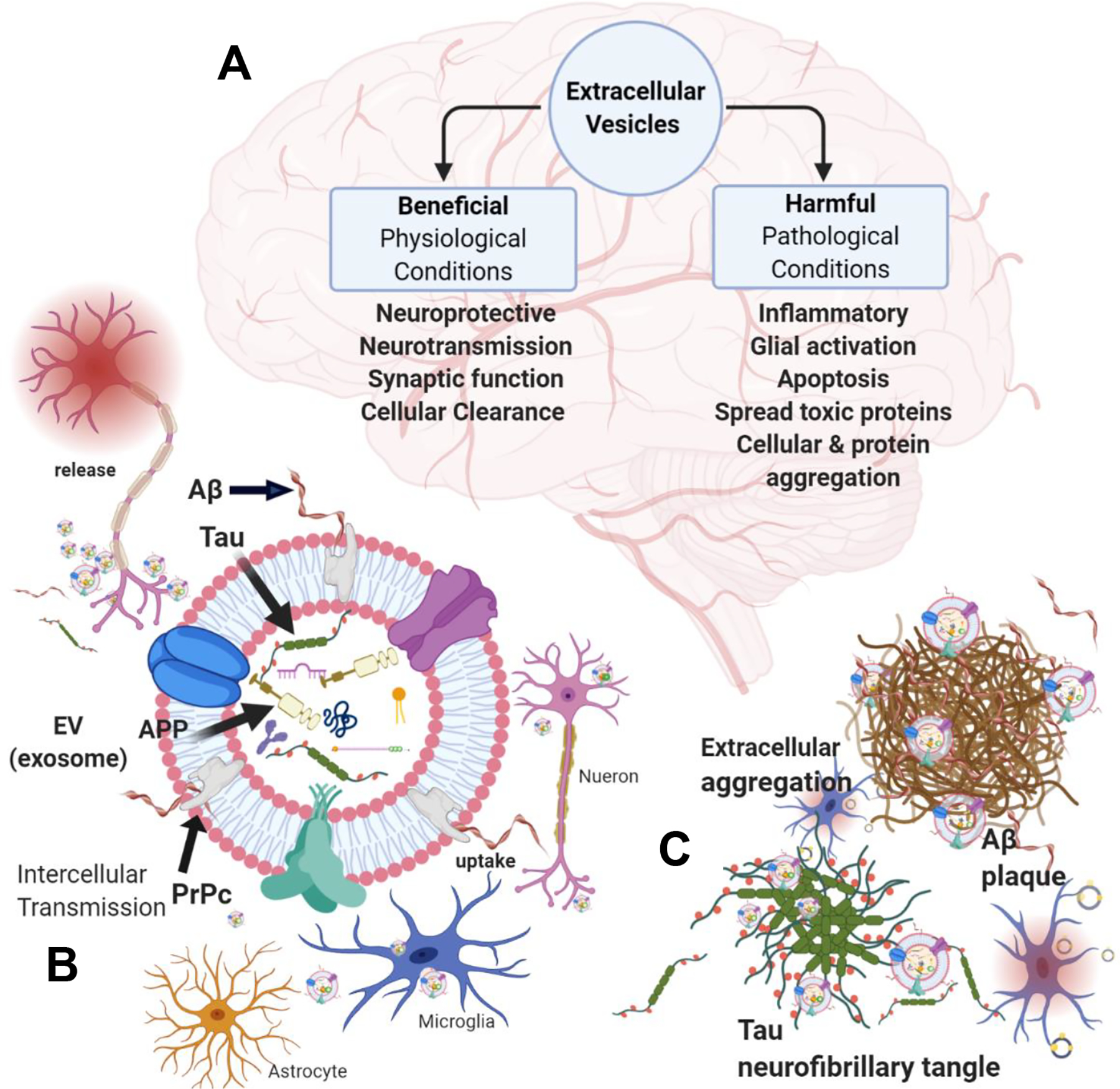
A: Under physiological conditions, EVs help maintain brain homeostasis and neuronal function. However, under pathological conditions, EVs may promote inflammation, neurodegeneration, and myelin loss and serve as conduits for the intercellular spread and aggregation of neurotoxic proteins. B: Neurons release EVs that can contain tau protein or carry Aβ fibrils anchored apically to membrane-bound PrPc. Microglia, astrocytes, and other neurons participate in the clearance and uptake of neuronal-derived EVs. C: EVs can seed the aggregation of extracellular free tau and Aβ, forming neurofibrillary tangles and plaques that activate microglia and promote microglial EV uptake.
