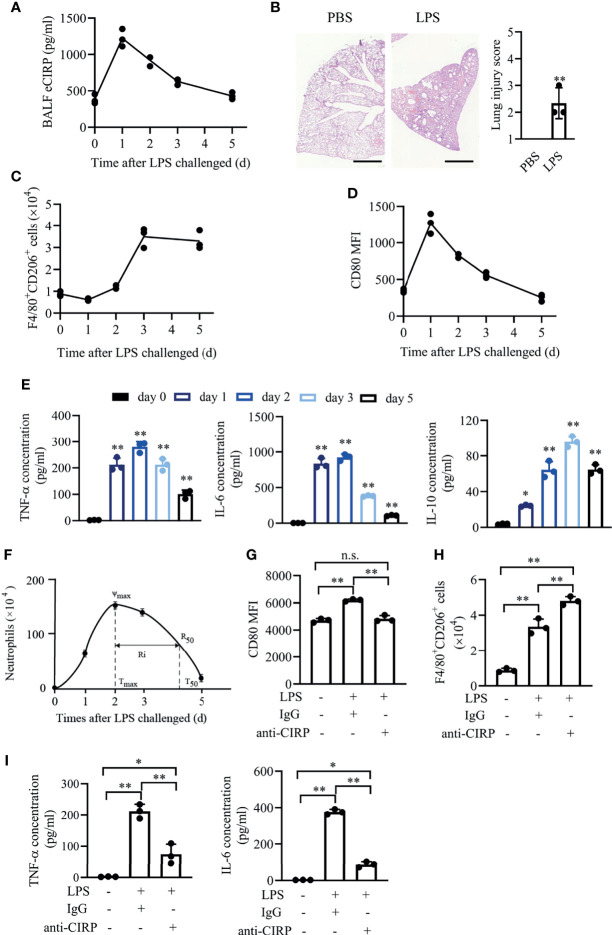
Figure 1.
eCIRP is temporally activated in acute lung injury. WT mice (n = 8 for each time point) were treated with 3 mg/kg LPS (i.t.) at the indicated times (days 0, 1, 2, 3, and 5). (A) The concentrations of BALF eCIRP were measured by ELISA at the indicated time after LPS administration i.t. (B) Lung tissue samples from mice with LPS or PBS administration for 24 h were dissected and subjected to H&E staining. Left panel: representative lung tissue images. Right panel: histopathological mean lung injury scores from each group. Scale bar: 1,000 µm. Measurements were performed in triplicate for data analysis. **P <0.01 vs. PBS group. Macrophages (F4/80+Ly-6G-) in BALF from WT mice were collected at 0, 1, 2, 3, and 5 days after i.t. LPS (3 mg/kg) challenge, and the number of CD206+ (C) macrophages and the MFIs of CD80 (D) in BALF macrophages were measured by FACS. (E) The concentrations of secreted TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 in BALF at the indicated time were measured. (F) The time course of neutrophil (Ly6G+F4/80-) numbers in BALF and resolution indices was calculated by flow cytometry. WT mice were administered LPS (3 mg/kg, i.t.) and then were treated with IgG or anti-CIRP antibody (1 mg/kg/day) via caudal vein for 3 days. Control mice were administered PBS. The macrophages’ MFIs of CD80 (G), the number of CD206+ macrophages (H), and cytokine expression (I) in BALF at day 3 after LPS treatment were measured (n = 3). Data are representative of at least two independent experiments. Results were expressed as mean ± SD. n.s., not statistically significant., *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared to 0 h group. Statistics: unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test (B), one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test for multiple comparisons (E, G–I). eCIRP, extracellular cold-inducible RNA-binding protein; WT, wild type; BALF, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; ELISA, enzyme linked immunosorbent assay; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; FACS, fluorescence activated cell sorter.