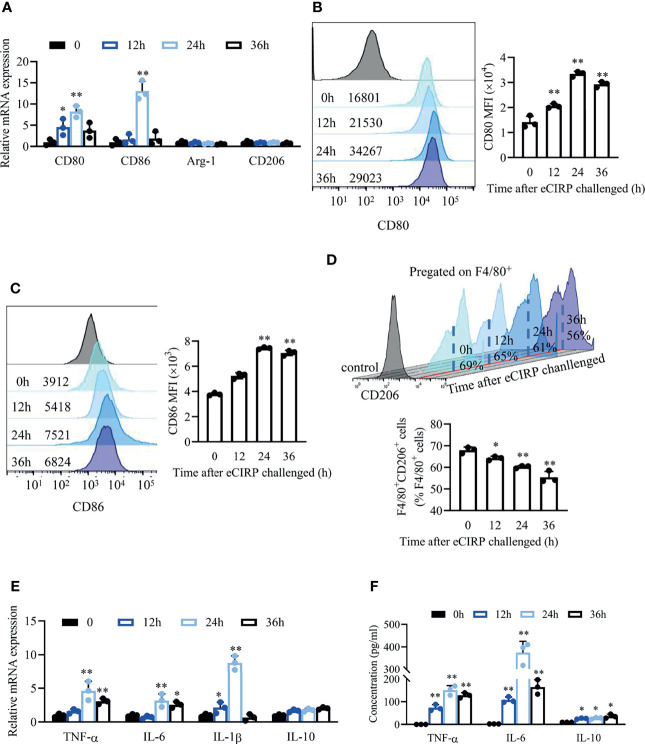
Figure 2.
eCIRP impaired/restrained M2 macrophage polarization and induced a pro-inflammatory response. (A) A qPCR assay was conducted to evaluate the mRNA expression of CD80, CD86, Arg1, and CD206 in BMDMs after eCIRP treatment for 0, 12, 24, and 36 h (n = 3). The MFI of CD80 (B) and CD86 (C) and the percentage of CD206+ macrophages in BMDMs (D) were measured by FACS at indicated time after eCIRP administration (n = 3). (E) A qPCR assay was conducted to evaluate the mRNA expression of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and IL-10 in BMDMs after eCIRP treatment at the indicated time (n = 3). (F) The concentrations of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 in the supernatant at indicated time after eCIRP administration were measured. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments. Results were expressed as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared to 0 h group. Statistics: One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test for multiple comparisons (A–F). eCIRP, extracellular cold-inducible RNA-binding protein; PCR, Polymerase Chain Reaction; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity; BMDM, bone marrow derived macrophage; FACS, fluorescence activated cell sorter.