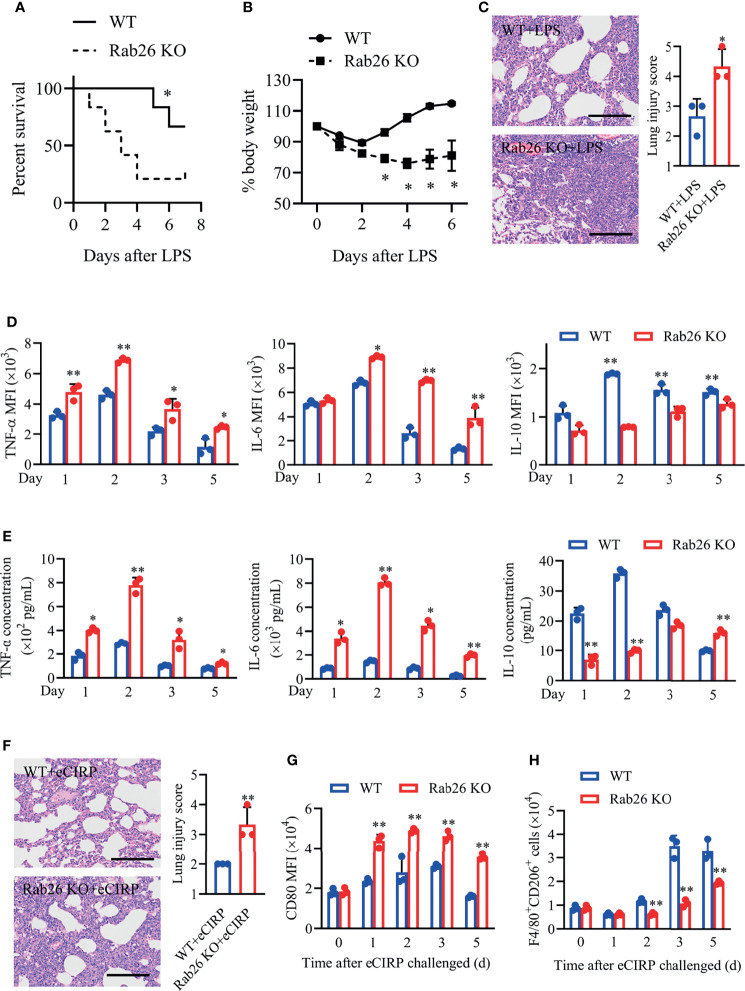
Figure 5.
Rab26 is critical for the eCIRP-mediated inflammatory response in lung injury. (A) Rab26-/- and WT mice were challenged with 10 mg/kg LPS i.t., and survival was monitored (n = 6). (B) Rab26-/- and WT mice were treated with 3 mg/kg LPS (i.t.). Change in body weight was monitored over 6 days (presented as % change from initial body weight) (n = 4 for each group). (C) Lung tissue samples from mice with LPS administration for 48 h were dissected and subjected to H&E staining. Lung injury scores were analyzed (n = 3). Scale bar: 150 µm. Macrophages (F4/80+) in BALF from WT and Rab26-/- mice were collected at days 1, 2, 3, and 5 after eCIRP (1 mg/kg, i.t.) challenge. The MFIs of intracellular TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 in BALF macrophages (D) and the concentrations of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 in BALF (E) at indicated time were measured (n = 3). (F) Rab26-/- and WT mice were treated with 1 mg/kg eCIRP (i.t.) at the indicated times. Lung tissue samples from mice with eCIRP administration for 48 h were dissected and subjected to H&E staining. Lung injury scores in each group were analyzed (n = 3). Scale bar: 150 µm. The MFIs of CD80 in BALF macrophages (G) and the number of F4/80+CD206+ macrophages (H) were measured by FACS (n = 3). Data are representative of at least two independent experiments. Results were expressed as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. the WT group at indicated time. Statistics: Log-rank test (A) or unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test (B–G). LPS, lipopolysaccharide; BALF, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; eCIRP, extracellular cold-inducible RNA-binding protein; WT, wild type; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity; FACS, fluorescence activated cell sorter.