Fig. 1. Performance of individual subjects on the Delayed Recognition Span Task.
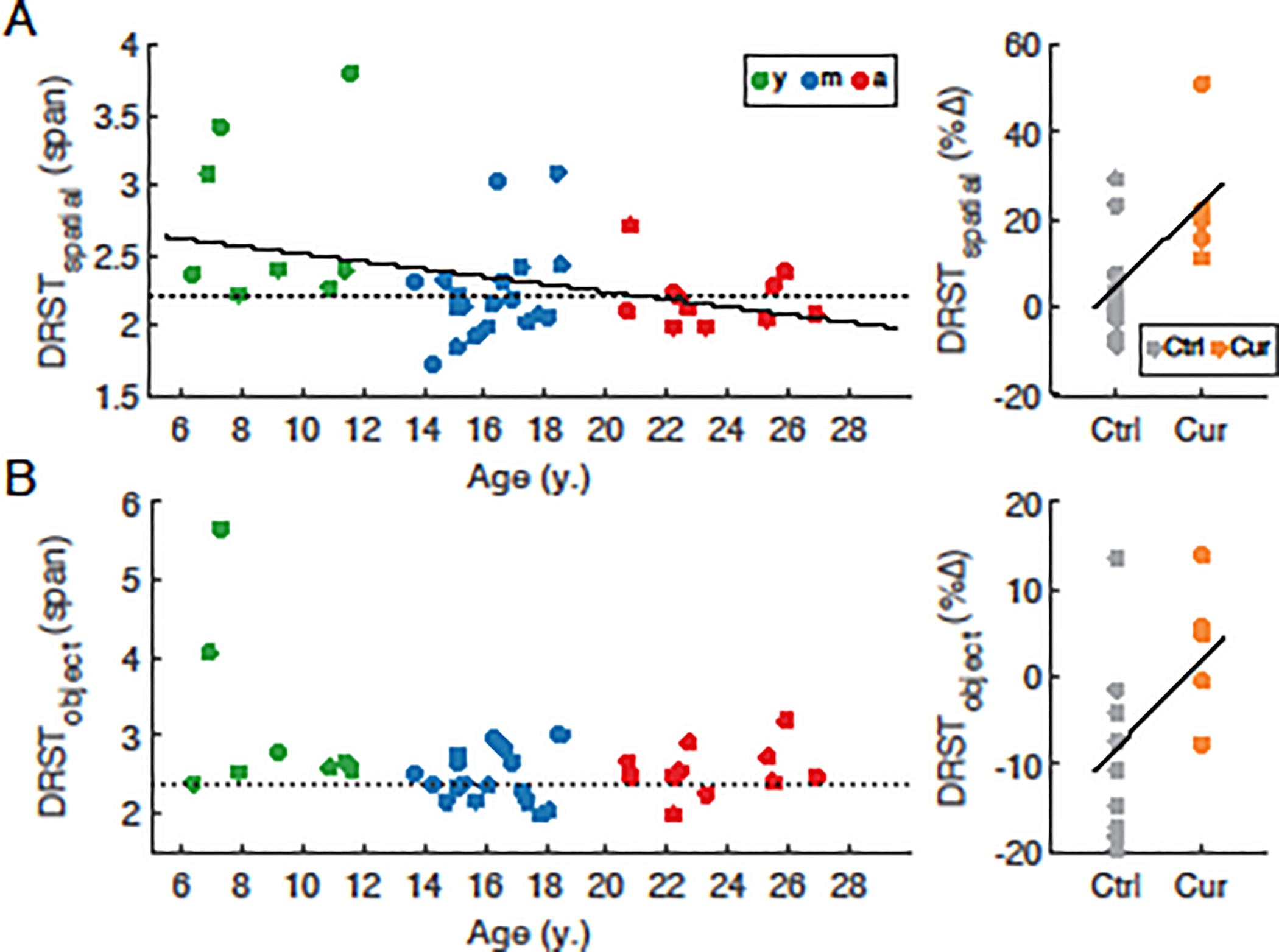
(A) left: DRST-Spatial span vs. age in young (y, green), middle-aged (m, blue), and aged (a, red) subjects; right: greater improvement in DRST-Spatial span in the curcumin-treated middle-aged cohort. (B) left: DRST-Object span in the same cohort of monkeys as in (A); right: greater improvement in DRST-object span in the curcumin-treated middle-aged cohort. Dotted lines denote performance threshold below which subjects are classified as impaired on each task. Solid lines denote statistically significant regressions (p<0.05). Data were obtained from a total of 8 young, 19 middle-aged control, 12 aged, and 7 middle-aged curcumin-treated monkeys.
