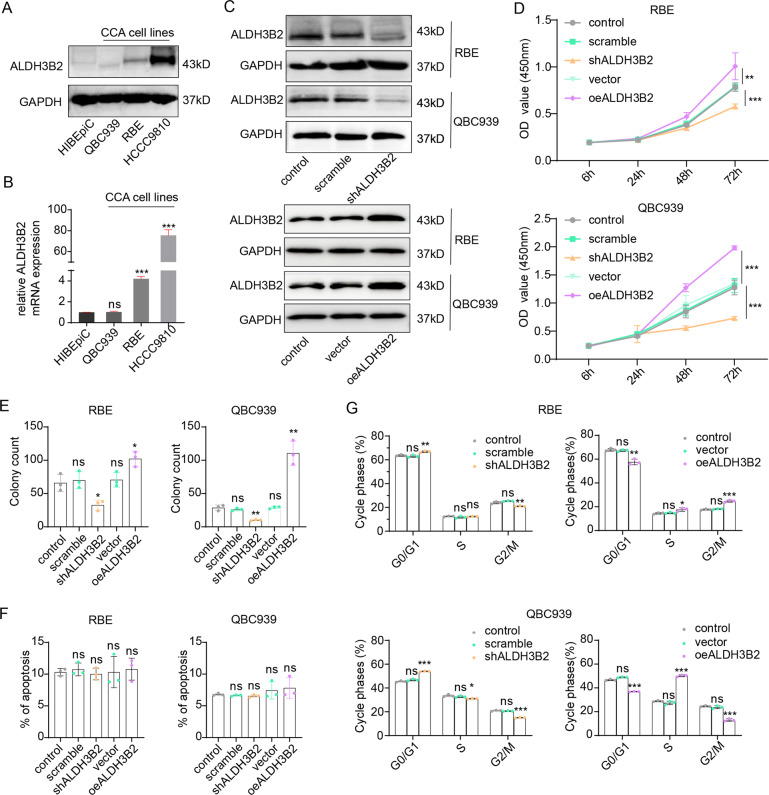
Fig. 2. ALDH3B2 promotes the cell proliferation ability of CCA by promoting the G1/S phase transition in vitro.
A, B Expression levels of ALDH3B2 in the human bile duct cell line HIBEpiC and CCA cell lines QBC939, RBE, and HCCC9810 were detected by western blot (A) and qRT-PCR (B). ALDH3B2 expression was upregulated in RBE and HCCC9810 CCA cell lines. C Western blot analysis of the knockdown and overexpression efficiency of ALDH3B2 in RBE and QBC939 cells. ALDH3B2 was successfully knocked down (upper) or overexpressed (lower) in these two cell lines. D CCK-8 assays were performed to identify the alteration in cell proliferation ability after ALDH3B2 knockdown or overexpression in RBE (upper) and QBC939 (lower) cells. E Clone formation of cells with ALDH3B2 knockdown or overexpression compared with their vector controls in RBE (left) and QBC939 cells (right). Knockdown of ALDH3B2 inhibited cell clone formation, while overexpression of ALDH3B2 promoted cell clone formation in vitro. F Flow cytometry was performed for detecting apoptotic rates in ALDH3B2-overexpressing and knockdown RBE (left) and QBC939 cells (right) cells. ALDH3B2 did not affect the apoptotic rates in these two cell lines. ns: no significance. G The effects of ALDH3B2 on the cell cycle were detected with flow cytometry after ALDH3B2 knockdown (left) or overexpression (right) in RBE (upper) and QBC939 cells (lower). Knockdown of ALDH3B2 inhibited the transition of the cell cycle from G1 to S phase, while overexpression of ALDH3B2 promoted the transition from G1 to S phase in vitro. ns: no significance; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.