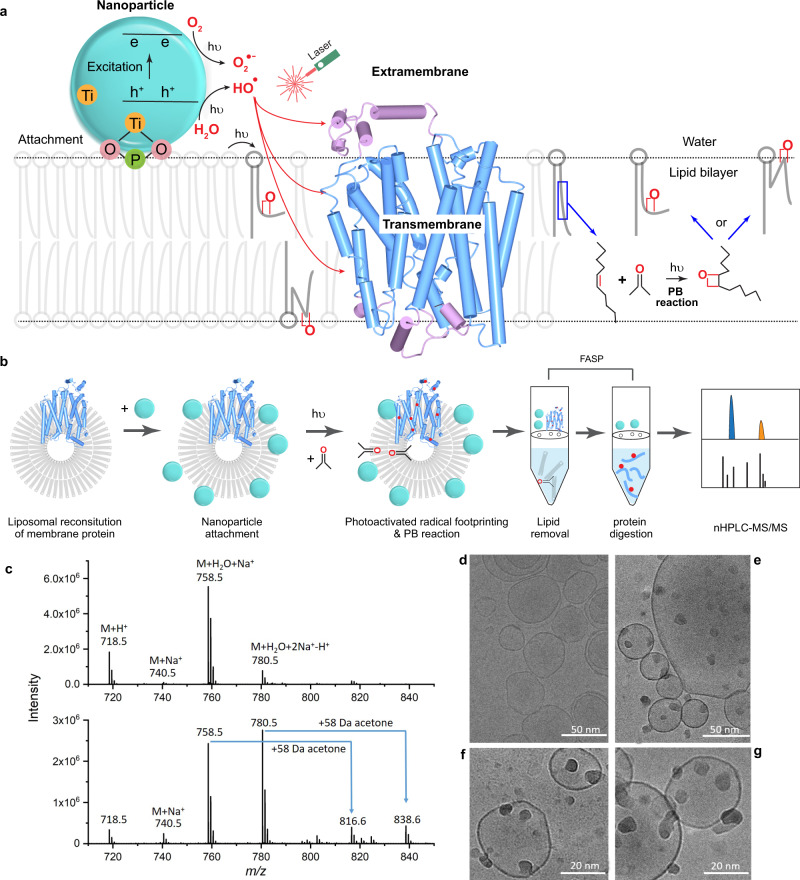
Fig. 1. Workflow and characterization of NanoPOMP.
a Scheme of NanoPOMP for IMP stabilized in liposome. TiO2 NPs are attached to the phosphate groups on the lipid bilayer. The liposome containing the IMP is irradiated with a 248 nm KrF laser, generating radicals (red dots). The PB reaction of acetone and lipid double bonds generates kinks in bilayer by a reaction mechanism shown on the right. b Typical workflow for the NanoPOMP experiment. (Although the protein is positioned in both orientations with equal probability in a liposome, we show only one orientation as an example.) c Upper: zoomed ESI mass spectrum of POPE and acetone/H2O; lower: ESI mass spectrum of POPE and acetone/H2O induced by NanoPOMP laser. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. d Cryo-EM image of liposome. e–g Cryo-EM images of TiO2 NPs (dark small spheres) attached to the liposome (large spheres), demonstrating liposome stability upon adsorption of NPs onto the surface. Higher magnification is shown in (f, g) for different sections of a cryo-EM grid. Experiments of d–g are repeated twice independently with similiar results.