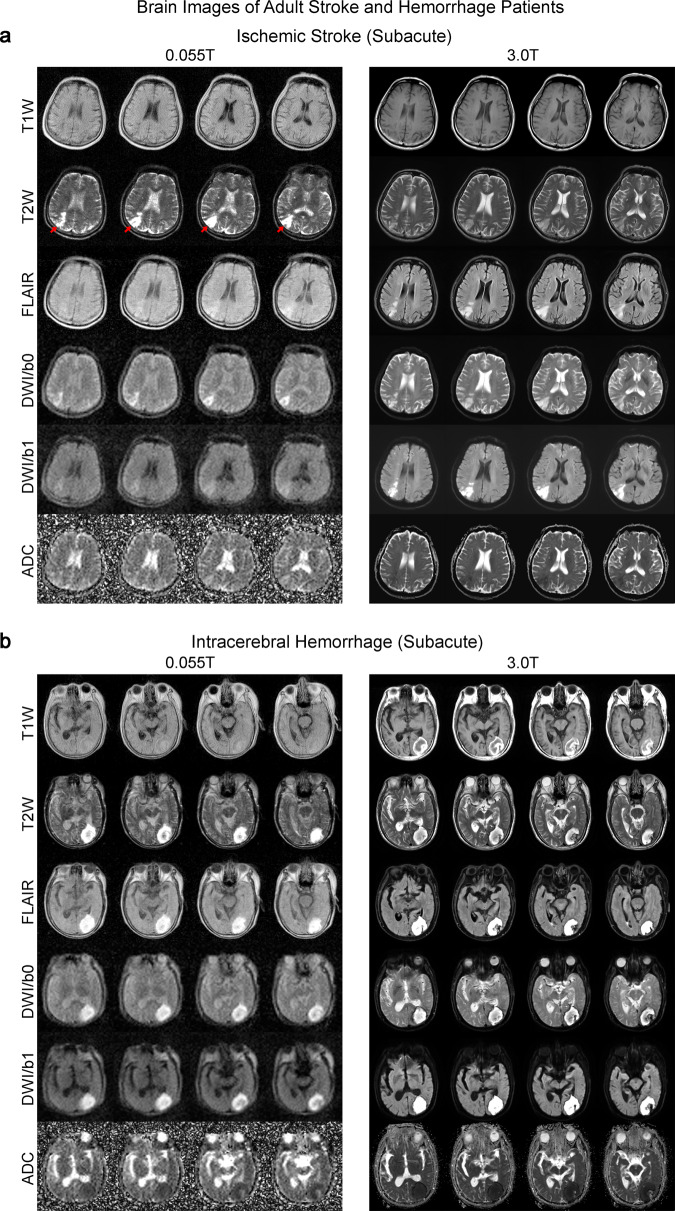
Fig. 7. Clinical utility of 0.055 T MRI for examining ischemic stroke and intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) patients.
Total 0.055 T scan time was ~30 mins for each patient. The patients were also scanned by a clinical 3 T MRI using the standard clinical protocols (~20 mins total scan time). a Subacute (~3 weeks) ischemic stroke patient (67 yrs. old; male). Note that 3 T clinical brain images were acquired 3 weeks prior to those acquired at 0.055 T. Ischemic infarct in the right parietal cortex (indicated by red arrows) was hyperintense in T2 and FLAIR images at 0.055 T and 3 T. Further, infarct was mildly hyperintense at ULF DWI, whereas it was hyperintense at 3 T. ADC showed slight hyperintensity at 0.055 T and hypointensity at 3 T. The corresponding signal changes for DWI and ADC maps at 0.055 T and 3 T are highly consistent with the expected progression of ischemic stroke across different timepoints (i.e., subacute vs. acute)32. b Subacute (~3 weeks) ICH patient (81 yrs. old; male). 0.055 T and 3 T images were acquired on the same day. Hematoma was visible in the left occipital lobe at 0.055 T and 3 T. It showed a hyperintense rim with a hypointense core in T2W images, indicating blood product and/or hemosiderin of different stages at the rim and core regions.