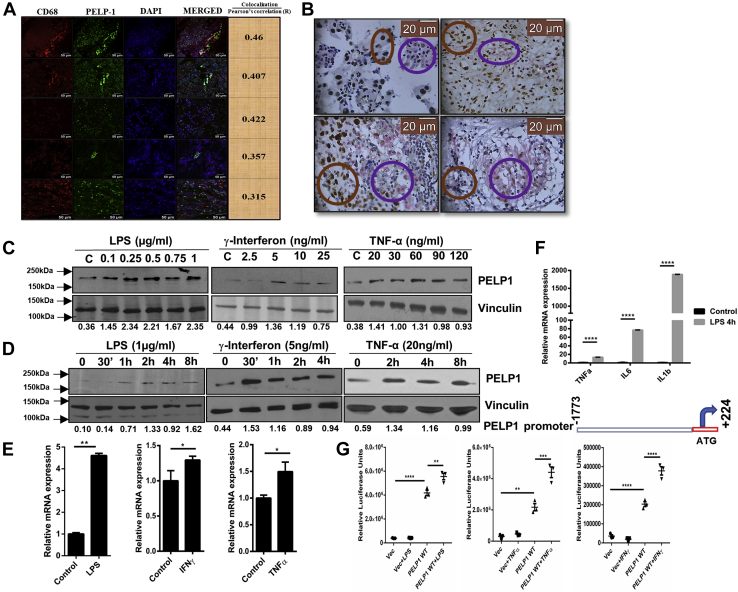
Figure 1.
PELP1 is an inflammatory responsive gene.A and B, representative double immunofluorescence (IF) images and double IHC images to show the expression of PELP1 in CD-68 positive cells in inflammatory breast tumor. In double IF, PELP1 was detected with Alexa Fluor 488 (green) and CD68 with Alexa Fluor 546 (red). The merged images show the coexpressed cells in yellow (the mean Pearson's correlation coefficient was calculated to be 0.2481, n = 13). For double IHC, PELP1 expression was nuclear localized as seen in DAB-positive cells, and CD68 was found mostly in the cytoplasm in close vicinity to the tumor as seen in Alk positive cells. The brown rings in (B) show the PELP1-positive regions, and magenta rings show the CD68-positive regions. The mean coexpression percentage of cells expressing both PELP1 and CD68 was calculated to be 23.85% (n = 13). C and D, Western blot images of PELP1 from RAW 264.7 cells treated with LPS, IFN-γ, and TNF-α in a concentration-dependent and time-dependent manner with vinculin as a loading control. E, PELP1 mRNA expression normalized with β-actin from RAW 264.7 cells treated with LPS (1 μg/ml) for 4 h and IFN-γ (5 ng/ml) and TNF-α (20 ng/ml) for 8 h time intervals. F, quantitative RT–PCR analysis showing the expression of three different inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β) under LPS (1 μg/ml for 4 h) treatment in RAW 264.7 cells. The expression of β-actin was used for normalization. G, top, schematic representation of PELP1 promoter cloned upstream of luciferase gene in the multiple cloning site (MCS) of pGL3 basic vector using HindIII and XhoI restriction sites. Bottom, relative luciferase activity of PELP1 promoter in RAW 264.7 cells on treatment with LPS (1 μg/ml for 4 h), TNF-α (30 ng/ml for 8 h), and IFN-γ (5 ng/ml for 8 h). For all the experiments, the data are represented as mean ± SEM and ∗ (p ≤ 0.05), ∗∗ (p ≤ 0.01), ∗∗∗ (p ≤ 0.001), and ∗∗∗∗ (p < 0.0001) for presenting p values (unless otherwise specified). DAB, 3,3′-diaminobenzidine; IFN-γ, interferon gamma; IHC, immunohistochemistry; IL, interleukin; LPS, lipopolysacharide; PELP1, proline, glutamic acid, and leucine-rich protein 1; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha.