Figure 3.
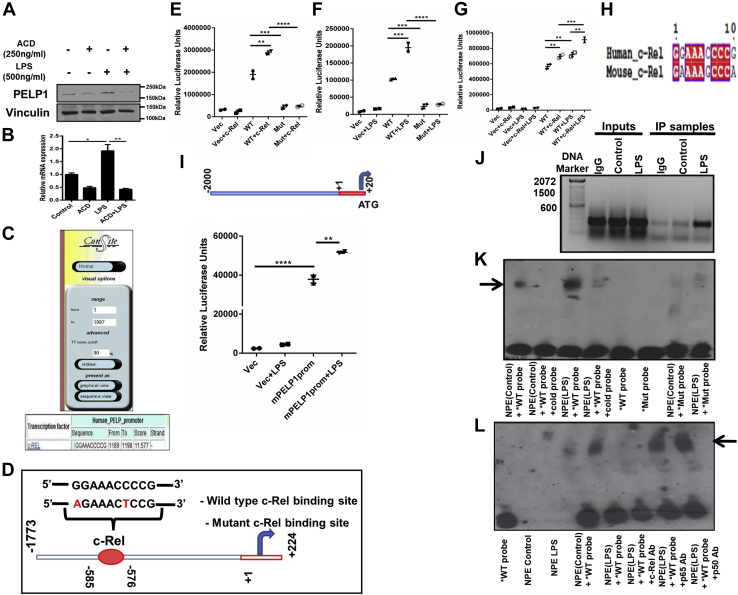
c-Rel is the specific transcription factor regulating PELP1 expression.A and B, Western blot and quantitative RT–PCR data of PELP1 in RAW 264.7 cells on LPS (1 μg/ml) treatment when pretreated with actinomycin-D (250 ng/ml) for 4 h. C, sequence analysis of mouse PELP1 promoter for potential transcription factor binding sites using ConSite. D, schematic representation of recruitment of c-Rel onto the consensus sequence present in PELP1 promoter along with mutated binding sites, which were highlighted. E–G, relative luciferase activity of PELP1 promoter from RAW 264.7 cotransfected with either PELP1 WT or mutant (Mut) promoter and c-Rel expression plasmids along with or without LPS (500 ng/ml) treatment. H, the c-Rel-binding consensus sequence from human PELP1 promoter was compared with the c-Rel-binding sequence in mouse PELP1 promoter using three different multiple sequence alignment programs (MAFFT, T-COFFEE, and ESPript 3.0) that showed 80% similarity between the two c-Rel-binding sequences. I, schematic representation of mouse PELP1 promoter cloned upstream of luciferase gene in the multiple cloning site (MCS) of pGL3 basic vector using KpnI and NheI restriction sites and relative luciferase activity of mouse PELP1 promoter on treatment with LPS of 1 μg/ml concentration for 4 h. J, in vivo ChIP assay—an agarose gel image of PCR products obtained from immunoprecipitated chromatin of LPS-treated and untreated RAW 264.7 cells using anti c-Rel antibody and simultaneous extraction of DNA followed by PCR amplification using ChIP-specific PELP1 promoter primers (forward 5′-TTGGTGGAGGCCTTTG-3′, reverse 5′-GTTTCCGGAGGTGGTT-3′). K, in vitro EMSA assay using nuclear protein extracts (NPEs) from LPS-treated and untreated RAW 264.7 cells incubated with biotinylated WT probes either with or without nonbiotinylated WT probes (cold probes) in higher concentration to biotinylated WT probes and mutant biotinylated probes (Mut probes). L, super shift EMSA assay in which DNA–protein complexes were further incubated with protein-specific antibody (here, its anti-c-Rel antibody) or negative control antibodies (anti-p65 and anti-p50 antibodies) to observe either band shift or band disappearance. We observed disappearance of the specific band when the probe, and nuclear protein complexes were incubated with c-Rel-specific antibody. The bold arrow represents specific band of interest. ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; PELP1, proline, glutamic acid, and leucine-rich protein 1.