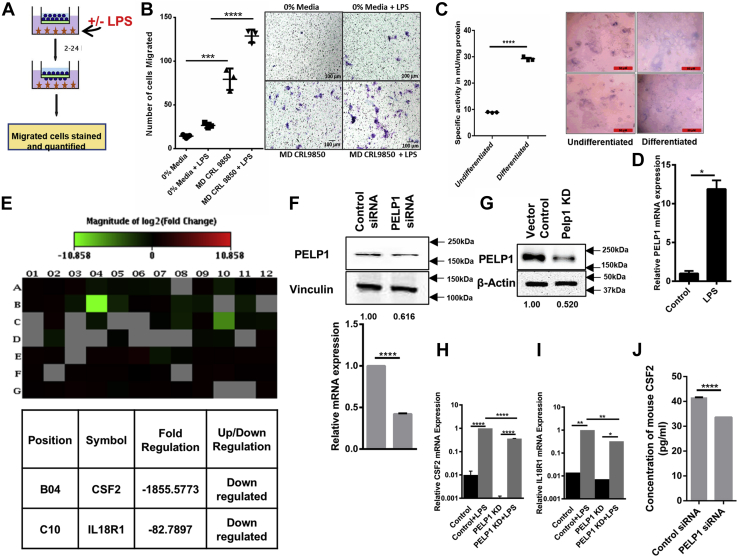
Figure 5.
GM-CSF—a new molecular target of PELP1.A, the schematic represents coculturing of Caco2 cells with MD-CRL9850 (with/without LPS) in a transwell migration apparatus. B, left, scattergram represents the number of migrated Caco2 cells when cocultured with 0% media, 0% media with LPS, LPS (1 μg/ml) treated/untreated MD-CRL 9850 cells. Right, representative phase contrast images of migrated Caco2 cells. C, left, specific activity of alkaline phosphatase (mU/mg of protein) in undifferentiated and differentiated Caco2 cells. Right, representative phase contrast images of Caco2 cells. D, quantitative RT (qRT)–PCR analysis of PELP1 in LPS-treated and untreated MD-CRL9850. E, heat map showing the expression of 84 key regulatory genes in mouse IL-6/STAT3 inflammatory signaling pathway determined by using PELP1 knocked down RAW 264.7 lysate. Green and red color backgrounds indicate the downregulation and upregulation of specific gene expressions, respectively. The position, gene symbol, and fold change of genes downregulated in PELP1 knockdown condition were represented below the heat map. F, Western blot and qRT–PCR images that confirmed PELP1 KD when RAW 264.7 cells were transfected with PELP1 siRNA. G, Western blot that confirmed PELP1 KD by shRNA lentiviral particles in RAW 264.7. H–I, validation of GM-CSF and IL18R1 expression by qRT–PCR using RNA from RAW 264.7 PELP1 KD clone with and without LPS induction. J, cell culture supernatants from PELP1 siRNA-transfected RAW 264.7 cells were collected after 48 h of transfection and assessed for GM-CSF concentration (pg/ml) using ELISA. GM-CSF, granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IL, interleukin; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; PELP1, proline, glutamic acid, and leucine-rich protein 1; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.