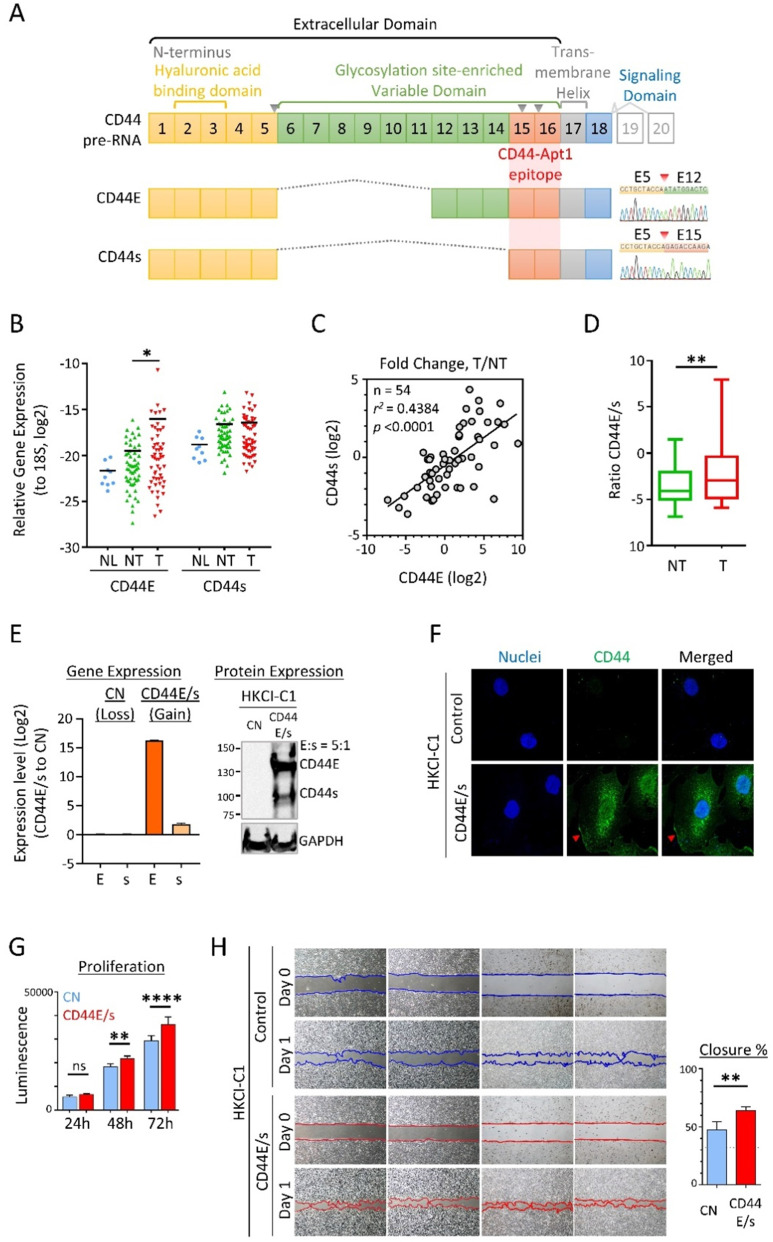
Figure 1.
(A) Gene structure and protein domain arrangement of CD44 and two prevalent isoforms CD44E and CD44s in HCC. CD44 consists of 20 exons. Exons 1-5 (yellow box) and 15-18 encode the standard isoform CD44s and are conserved in both isoforms. Exons 1-15 depict the extracellular domain with Exons 2-3 for the hyaluronan binding domain and Exons 6-14 (green box) for the variant domain harboring abundant glycosylation sites. Exon 17 (grey box) is for transmembrane helical domain, while Exon 18 (blue box) encodes the intracellular signaling transduction domain. Exons 19 and 20 (grey open box) are mutually exclusive exons. Alternative splicing between Exons 5 and 15 resulted in the CD44E isoform. Supporting sequencing traces for the detection of CD44s and CD44E isoforms in HCC are provided. Epitope region bound by CD44-Apt1 is also suggested. Grey inverse triangles indicate reported MMP cleavage sites on CD44 protein. (B) Relative expression of CD44E and CD44s genes in nine human normal liver tissues (NL) and fifty-four pairs of HCC tumoral tissues (T) and adjacent non-tumoral tissues (NT). Expression is normalized to S18 ribosomal RNA. (C) Correlation in fold change (T/NT) between CD44s and CD44E gene expression. (D) Ratio of CD44E to CD44s in TN and T in HCC. (E) Establishment of CD44E- and CD44s-dual-overexpressed HCC stable cell line (CD44E/s). Gene expression of CD44E (E) and CD44s (s) in HKCI-C1 vector control (CN) and CD44E/s cells were determined by real-time quantitative PCR and compared between the two cell lines. For CD44 protein expression, 20 ug of total protein of either CN or CD44E/s cell lysates were resolved on a 5-12% gradient acrylamide gel. Membrane with proteins transferred from the gel was blotted with anti-CD44 or anti-GAPDH antibodies. GAPDH protein was used as an endogenous loading control. Relative quantity of CD44E to CD44s protein (E:s) was determined based on the their protein band intensities. (F) Localization of CD44 in the HKCI-C1 cells by confocal imaging. CD44 protein (green) in the CN and CD44E/s cells was stained with primary CD44 antibody and Alexa fluor-488 labeled secondary antibody. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue). The stained cells were imaged using confocal microscope under 100X magnification. Red arrows point to the membrane edge. (G) Proliferation potential of HKCI-C1 cells. The CN and CD44E/s cells were seeded at a density of 1000 per well. Cell viability was measured after 24, 48 and 72 hours using Celltiter-Glo. Luminescence signal plotted, mean ± SEM (n=8). Comparisons between CN and CD44E/s were done using 2-way ANOVA test with Bonferroni correction. (H) Migratory phenotype. HKCI-C1 CD44E/s and CN cells were seeded on two-chamber culture dish. Insert between the two chambers was removed at Hour 0. Bright field images were taken at Hour 0 and 13. Closure percent was calculated as the percentage of gap area that occupied by the cells between Day 0 and Day 1 (mean ± SD, n=4). Measurements were compared using paired t-test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001.