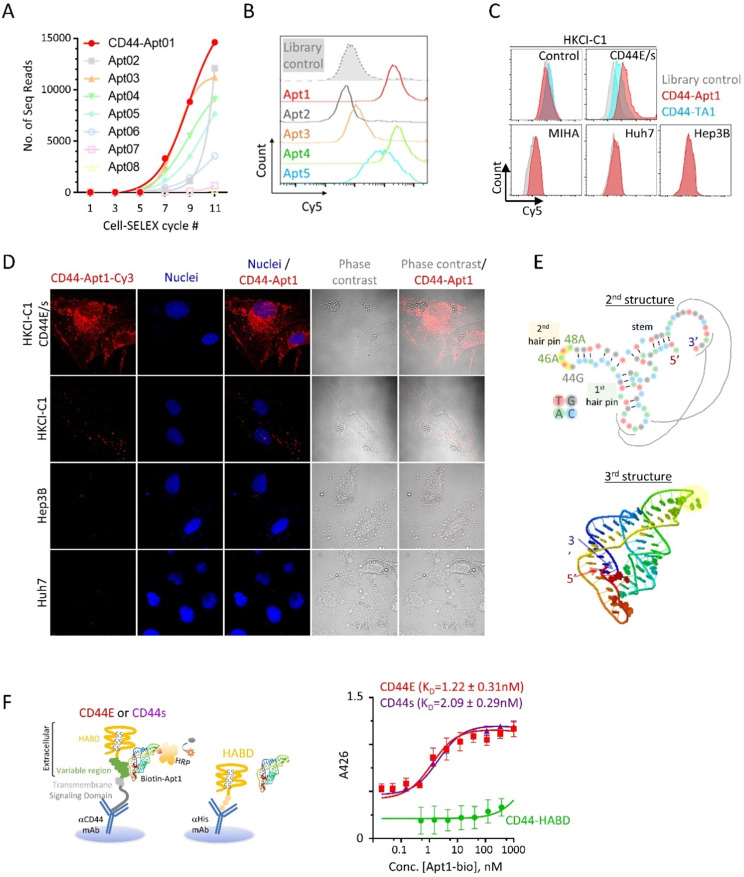
Figure 2.
Identification and characterization of CD44E/s aptamers. (A) Enrichment of CD44-specific aptamer sequences by the technique of loss-gain CELL-SELEX. Aptamer pools from alternative cycles during Cycle 1 to 11 were sequenced by next-generation sequencing. For the top eight abundant aptamers, named CD44-Apt1 to -Apt8, number of sequencing reads in different cycles were plotted to illustrate their gradual enrichment across the SELEX process. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of HKCI-C1 CD44E/s cells after incubation with Apt-1 to -Apt5 and library control. These 5 aptamers and aptamer library were conjugated with Cy5 fluorescence and incubated with HKCI-C1 CD44E/s cells at 200nM for 1 hour at room temperature with agitation before analyzing by flow-cytometry. Fluorescence intensity of Cy5 was plot in the histograms. (C) Flow cytometric analysis of various human liver cells after incubation with Cy5-labelled CD44-Apt1 aptamer. HKCI-C1 cells, including vector control and CD44E/s, and a normal liver cell line MIHA, and two CD44-negative HCC cell lines, Huh7 and Hep3B cell lines were stained with Cy5-labeled CD44-Apt1 (red), Cy5-labeled CD44 aptamer TA1 (blue) 20 or library control (grey) and analyzed by flow cytometry. Fluorescence intensity of Cy5 was plot in the histograms. (D) Confocal fluorescence microscopy of HCC cells for localization of CD44-Apt1. HKCI-C1 vector control and CD44E/s cells, Hep3B, and Huh7 were live-stained with Cy3-labeled CD44-Apt1 (red), and then fixed and imaged by confocal microscopy. Nuclei were stained using Hoechst (blue). Phase-contrast images were taken to illustrate the outline of cells. (E) Predicted secondary and tertiary structure of CD44-Apt1. Black lines indicate the nucleotide interaction between the loop of first hairpin and the sequence at the most 3' end when Apt1 folded into 3D structure. (F) Epitope mapping and binding affinity determination of CD44-Apt1 using sandwich ELISA. CD44E and CD44s proteins were captured on the bottom of ELISA plate using anti-CD44 antibody that targets COOH-terminal intracellular domain and remains the N-terminal extracellular domain intact for aptamer binding. His-tagged recombinant CD44 HABD protein was immobilized on ELISA plate using His-tag antibody. The captured CD44 proteins were incubated with various concentrations of biotin-labeled CD44-Apt1 (5 pM - 10 µM). Dissociation constant, KD was calculated based on the absorbance values from replicates (n=3) using the one-site binding model for non-linear regression in GraphPad.