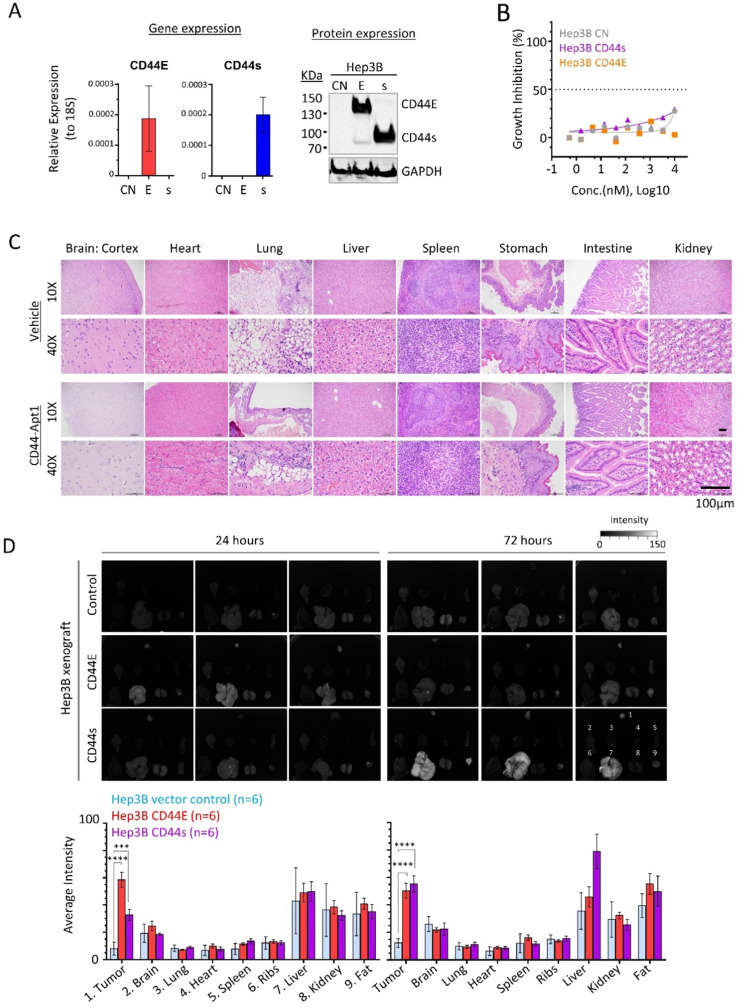
Figure 4.
In vivo homing and non-toxic nature of CD44-Apt1. (A) Establishment of CD44E- and CD44s-overexpressed Hep3B stable cell lines. (B) In vitro cytotoxicity of CD44-Apt1 on the Hep3B stable cell lines. Hep3B vector control (grey), CD44s-OE (purple), or CD44E-OE (orange) cells were incubated with various concentration of CD44-Apt1, ranging from 56 pM to 10 µM, for 72 hours. Cytotoxicity was represented in term of percentage of growth inhibition (mean ± SEM, n=3). (C) In vivo cytotoxicity. A total of 250 pmol of phosphorothioate-modified CD44-Apt1 or vehicle buffer was intravenously injected into Nude mice and incubated for 72 hours. Major organs, were harvested and processed for haemotoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining for histological imaging. (D) Ex-vivo fluorescence imaging of the HCC xenograft tumor and major organs of the aptamer-injected animals. HCC xenograft tumors were developed in Nude mice by subcutaneous injection of 5 x 106 cells of Hep3B vector control, CD44E-OE, or CD44s-OE cells. When xenograft reached size of about 200mm3, 250 pmol of Cy3-labeled CD44-Apt1 was intravenously injected into tumor-bearing mice and incubated for 24 or 72 hours before sacrifice. Fluorescence intensity was measured in the tumor and organs and compared between xenograft models using 2-way ANOVA test (mean ± SD, n=6). Two independent experiments were carried out with 3 mice per group. Another set of images were displayed in Supplementary Figure 2. **p <0.01, ***p<0.001.