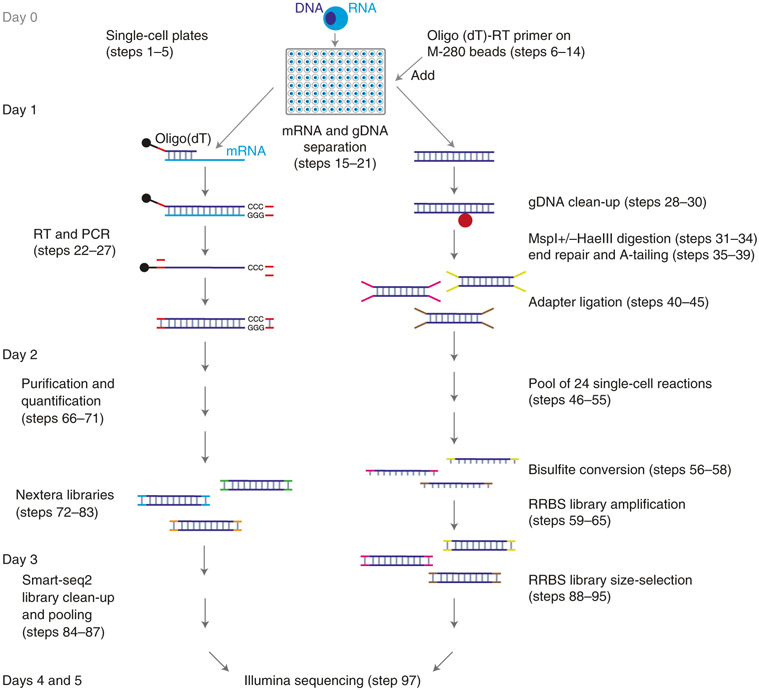
Fig. 1 ∣. Schematic overview of the Smart-RRBS protocol.
After deposition by flow cytometry of single cells into a 96-well plate containing lysis buffer and optional flash freezing and storage at −80 °C, poly(A)+ mRNAs are pulled down by using M-280 streptavidin beads (shown as black dots) coated with a 5′ biotinylated oligo(dT) RT primer. Genomic DNA (gDNA) in the supernatant is cleaned up on AMPure beads (shown as a red dot). After separation of mRNA from genomic DNA, single-cell RRBS and Smart-seq2 libraries are generated separately. Not counting the time it takes to sort cells into single-cell plates at the beginning (Steps 1-5) and to generate Illumina sequencing data at the end (Step 96), it takes ~3 d to carry out both branches of the Smart-RRBS protocol when Smart-seq2 and RRBS library construction steps are staggered as described in the step-by-step procedure.