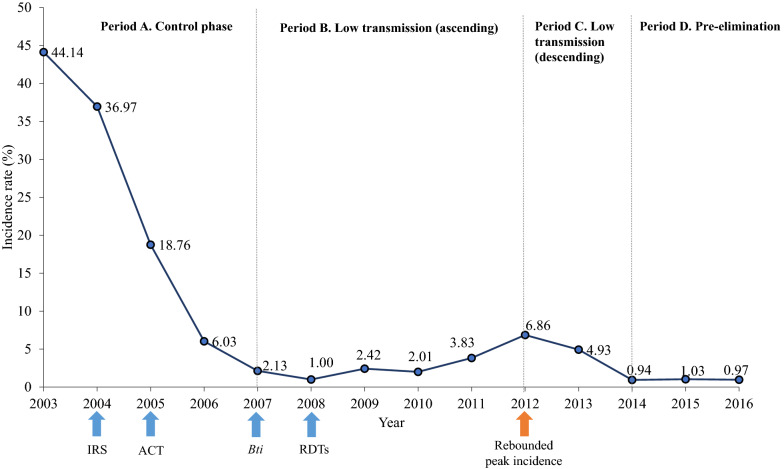
Fig. 3.
Classification of periods based on the annual malaria incidence rate in STP. Malaria incidence had dropped by 40% during the control phase from 2000 to 2007 due to the prompt deployment of indoor residual spraying (IRS), and the introduction of artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT). Between 2007 and 2012, the incidence rate was controlled under 5% by applying Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis (Bti) for larval control, and rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) for mass screening. Subsequently, there was a slight increase in the incidence, and the rebounded peak was shown in 2012. After the peak incidence, malaria incidence was again controlled to ~1% and reaching the pre-elimination phase