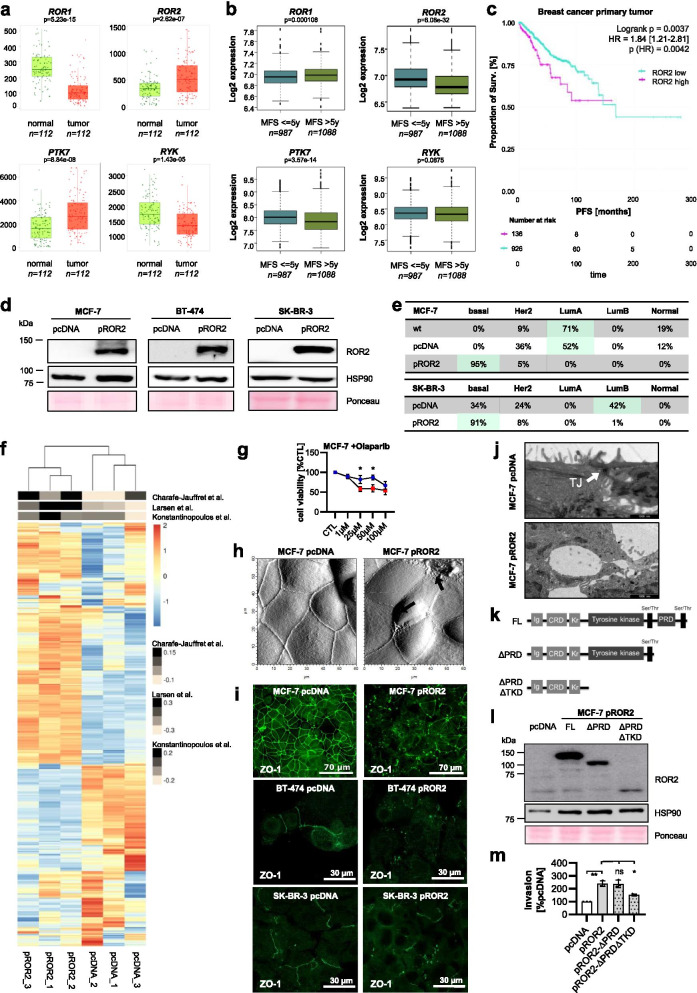
Fig. 1.
Expression of ROR2 induces a highly aggressive phenotype in breast cancer cells. a RNA-Seq: Gene expression of the four non-canonical WNT co-receptors ROR1, ROR2, PTK7 and RYK in normal breast (green) and matched breast cancer tissue (red) from the TNMplot database. Significance was calculated with a paired Wilcoxon statistical test. b Microarray gene expression data from 2075 breast cancer primary tumors were correlated with either poor (≤ 5 years) or better (> 5 years) metastasis-free survival (MFS). Significance was calculated with a t-test. Boxes represent the 25-75th percentiles with the line at the median. Outliers are marked as small dots. c Progression-free survival (PFS) of 1067 breast cancer patients from TCGA stratified by ROR2 mRNA expression. d MCF-7, BT-474 and SK-BR-3 human breast cancer cells were transfected either with an empty vector (pcDNA) or with a hROR2 overexpression plasmid (pROR2). Transfection efficiency was confirmed by western blot. e Determination of the molecular breast cancer subtype based on RNA-Seq data from the indicated cell lines using the PAM50 gene signature. f RNA-Seq of MCF-7 cells: GSVA analysis for three independently published BRCAness gene expression signatures. g MTT assay: Cells were treated for 96 h with the indicated concentrations of olaparib (mean ± SD, n = 3, *p < 0.05). h Atomic force microscopy (AFM) of MCF-7 pcDNA and pROR2 cells. i Immunofluorescence staining of the tight junction marker ZO-1. j Electron microscopy of a representative tight junction (TJ) in MCF-7 pcDNA cells. An example for a defective cell-cell-junction is shown for pROR2 cells (scale bar: 1 μm). k Schematic overview of the pROR2 C-terminal deletion constructs. l+m C-terminal deletion constructs were overexpressed in MCF-7. Expression was confirmed by western blot (l) and the invasion rate measured in Boyden chambers (m) (mean ± SD, n = 3, *p < 0.001, **p < 0.0001, ns = not significant). Significance was calculated with a one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test