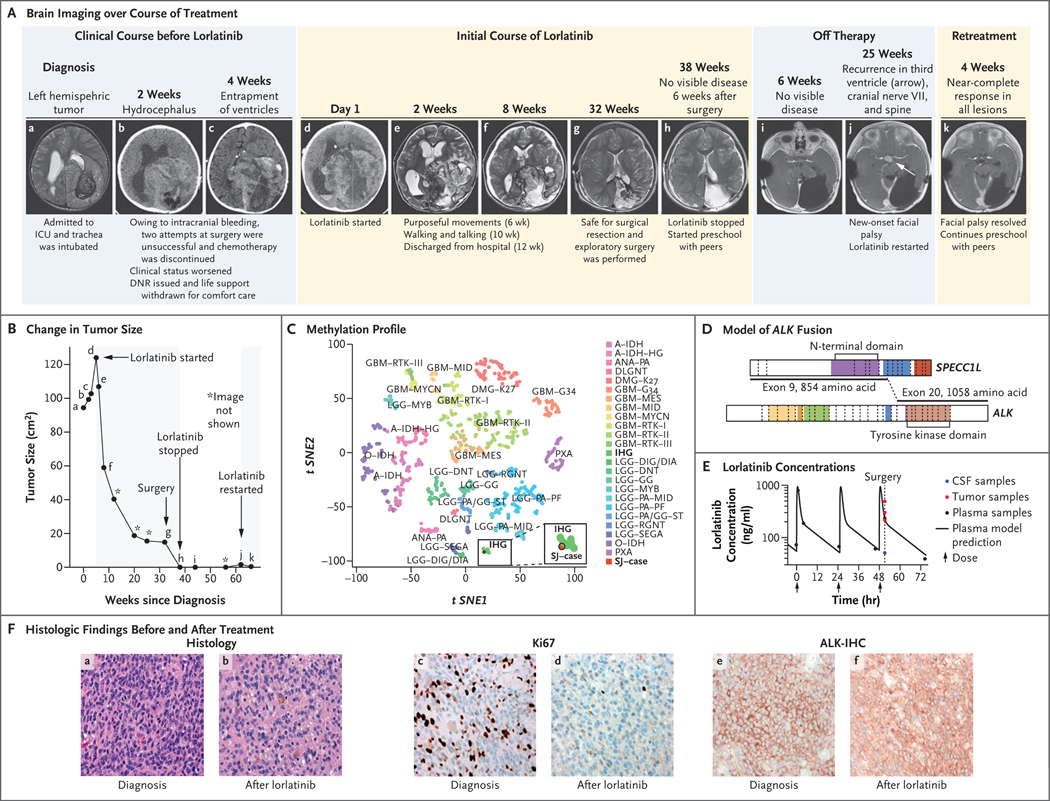
Figure 1. Response to Lorlatinib Treatment.
The clinical course of the patient is shown in serial brain imaging taken before (Panel A, subpanels a through c) and during (d through h) initial lorlatinib therapy. Subpanels i and j depict imaging after lorlatinib was discontinued, and subpanel k depicts the near-complete response of the recurrent tumor 4 weeks after retreatment with lorlatinib began. Panel B shows the change in the tumor size (black line) as a function of time and treatment; the black dots (a through k) correspond to the imaging studies shown in Panel A, and shaded areas denote periods of time the patient was receiving treatment with lorlatinib. Tumor size was determined by the product of the measurement of the longest tumor dimension and its perpendicular measurement. Panel C depicts the tumor sample (SJ–case) among infantile hemispheric gliomas (IHG) when projected on a t-statistic–based stochastic neighbor embedding (t-SNE) projection of a methylation data set of 1013 gliomas and glioneuronal tumors. Panel D shows a model reconstruction of the in-frame SPECC1L–ALK fusion that combined exons 1 through 9 of SPECC1L with exons 20 through 29 of ALK. The kinase domain of ALK (light brown) remained intact. Panel E shows the plasma concentration time of lorlatinib and the lorlatinib concentations in tumor tissue (red) and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF, blue). The y axis represents measured concentration of lorlatinib. The x axis represents time in hours; the arrows indicate the times when the patient was administered the medication. Panel F compares the diagnostic sample (a, c, and e) with the sample obtained after treatment with lorlatinib (b, d, and f). The diagnostic sample consisted of a compact, high-grade astrocytoma with mitotic activity (a) and a high proliferative index (c). Strong, diffuse expression of ALK was detected by immunohistochemistry (e). The recurrent tumor showed evidence of therapeutic response, including extensive infiltration by histiocytes (b) and a reduced proliferative index (d). Expression of ALK was retained in the recurrent tumor cells (f). DNR denotes do not resuscitate, and ICU intensive care unit. A key to the abbreviations for the methylation class shown in Panel C is provided in Table S1 of the Supplementary Appendix, available at NEJM.org.