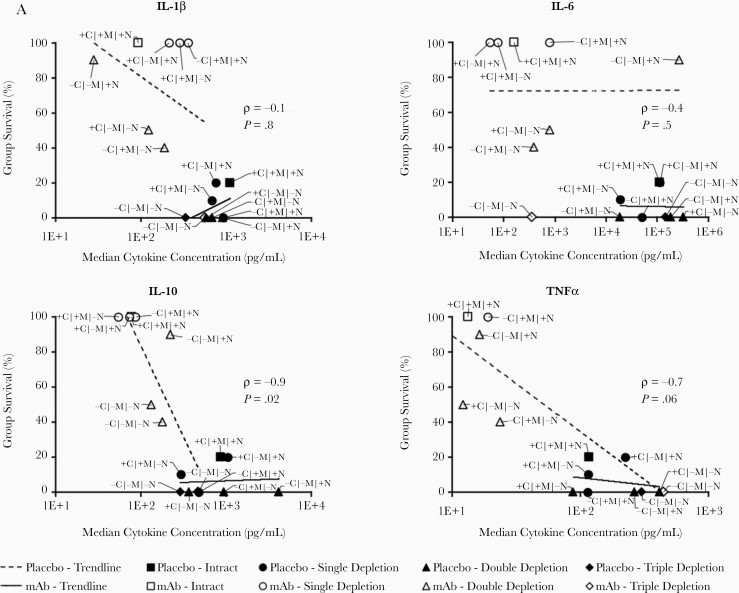
Figure 6.
IL-10 but not TNF-α is required for mice to survive lethal bacteremia with mAb therapy. A, Median cytokine concentrations at 9 hours postinfection for each group of mice (n = 8 mice per group) graphed against the survival for that group. White-filled symbols indicate mAb-treated groups and black-filled symbols are placebo groups. Trend lines are separately shown for mAb-treated and placebo mice. Spearman rank correlation coefficient (ρ) and P value are shown for the correlations between cytokine concentrations and survival for mAb-treated mice. B, TNF-α–KO and wild-type mice survived IV infection with 1×108 CFU Acinetobacter baumannii HUMC1 when treated with 5 μg mAb, whereas IL-10–KO mice could not be rescued (C); *P < .05 compared to all other groups. Blood was harvested at 7 hours postinfection to quantify bacterial burden in the blood and obtain plasma cytokine levels by multiplex Luminex assay. D, Bacterial burden in mAb-treated mice was no different in IL-10–KO than in wild-type mice; however, only the mAb-treated wild-type group survived. E, Cytokine analysis revealed that IL-10–KO mice generated higher levels of proinflammatory cytokines than wild-type mice in the same treatment group (n = 5 mice per group). D and E, Plots show medians and interquartile ranges. Abbreviations: −, depleted; +, not depleted; C, complement; CFU, colony-forming unit; IL, interleukin; IV, intravenously; KO, knockout; M, macrophages; mAb, monoclonal antibody; N, neutrophils; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α.