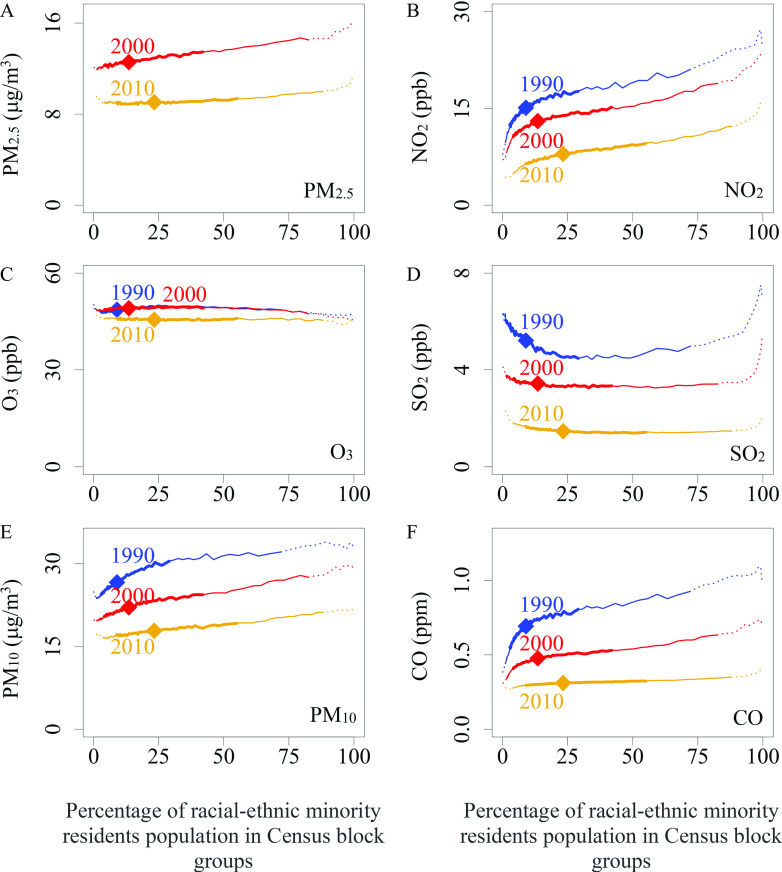
Figure 2.
Relationship between the proportion of racial/ethnic minority residents in census block groups and average criteria air pollution concentrations in the years 1990, 2000, and 2010 for (A) , (B) , (C) , (D) , (E) , and (F) CO. For each panel, the thicker portion of the line indicates the 25th to 75th percentile of census block groups, the thin line indicates the 10th to 90th percentiles, the dashed line indicates the 1st to 99th percentiles, and the diamond icon indicates the median. Note: CO, carbon monoxide; Hispanic, Hispanic people of any race(s); NH, non-Hispanic; , nitrogen dioxide; , ozone; , fine particulate matter with aerodynamic diameter less than or equal to ; ; , sulfur dioxide.