Figure 1.
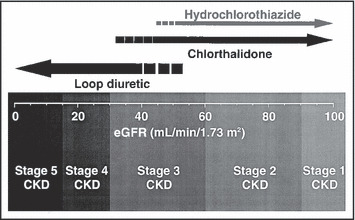
Selection of a diuretic based on the patient’s estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). Note that low‐dose hydrochlorothiazide is typically less effective when the eGFR is less than about 45 mL/min/1.73 m2 (using the simplified Modification of Diet in Renal Disease equation), 21 whereas low‐dose chlorthalidone begins to lose its antihypertensive efficacy at a somewhat lower threshold. In general, a loop diuretic is recommended for patients with an eGFR<35 mL/min/1.73 m2. The stages of chronic kidney disease (CKD) are based on the National Kidney Foundation’s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative guidelines. 22
