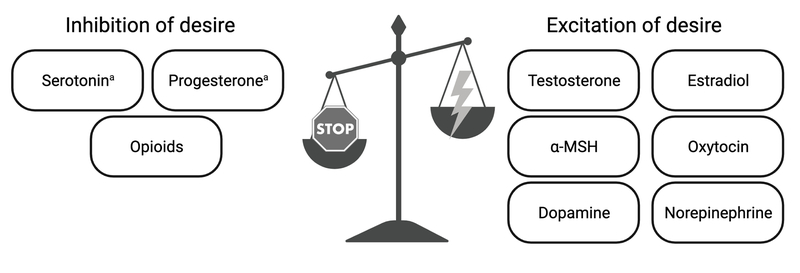
Figure 1.
Various physiological substrates and their role in either exciting or inhibiting sexual desire, based on the Dual-Control Model (Bancroft et al, 200915). Deficient excitation, excessive inhibition, or a mix of both can contribute to the physiology of hypoactive sexual desire disorder. aSerotonin and progesterone have both excitatory and inhibitory properties, though are usually considered inhibitory. α-MSH (alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone).