Fig. 2.
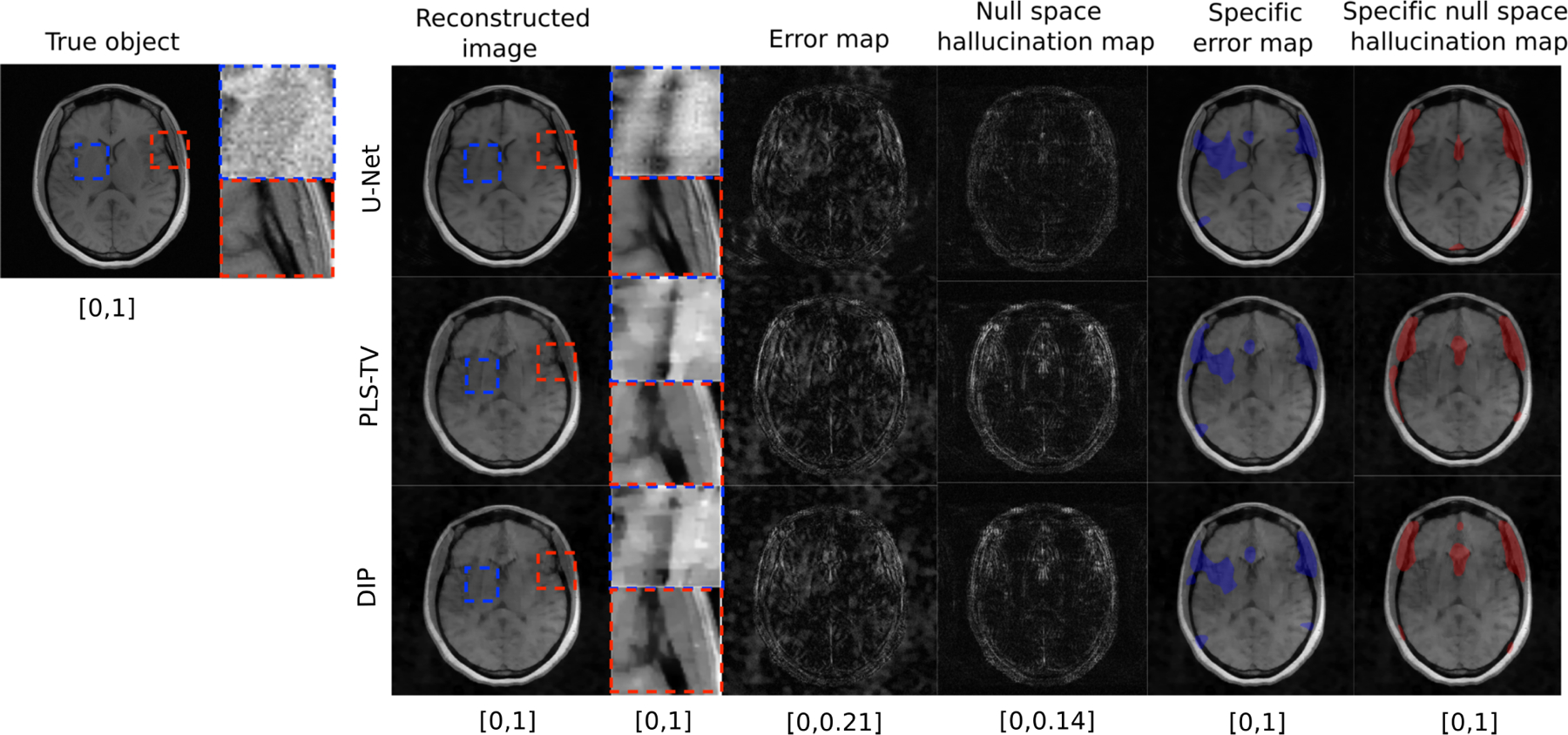
Example of a true object and reconstructed images along with error maps and hallucination maps (null space) for IND data with different reconstruction methods – U-Net (top), PLS-TV (middle) and DIP (bottom). Expanded regions are shown to the right of the reconstructed images. The specific error map (blue) and specific null space hallucinations map (red) are overlaid on the reconstructed images for each method. The image estimated by the U-Net method has visibly lower hallucinations in the null space compared to PLS-TV and DIP. The region within the red bounding box is one of the locations that contains hallucinations for all the reconstruction methods. In this region, the U-Net method shows mild hallucinations compared to PLS-TV and DIP. Fine structures in this region appear to be oversmoothed in the image estimates obtained by use of PLS-TV and DIP. A false structure is also shown (within the blue bounding box region) that appears for all the reconstruction methods due to the phase noise and not due to the imposed prior, and hence cannot be classified as a hallucination.
