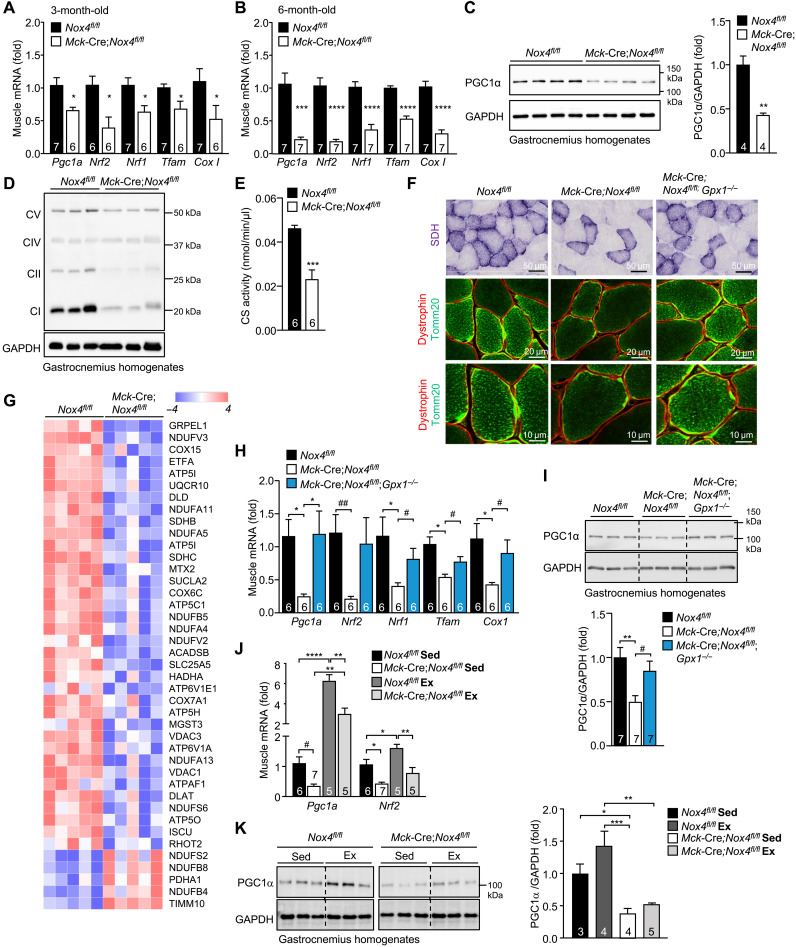
Fig. 4. NOX4-derived H2O2 in skeletal muscle is required for mitochondrial biogenesis.
(A to B) Gastrocnemius muscles from 3- or 6-month-old Nox4fl/fl and Mck-Cre;Nox4fl/fl chow-fed male mice were processed for qPCR monitoring for the expression of mitochondrial biogenesis genes. (C to F) Gastrocnemius muscle from 6-month-old Nox4fl/fl and Mck-Cre;Nox4fl/fl chow-fed male mice was homogenized and immunoblotted for (C) PGC1α and (D) total OXPHOS proteins [complexes (C) I to V] or processed for the analysis of (E) citrate synthase (CS) activity. (F) Gastrocnemius muscles from 6-month-old male Nox4fl/fl, Mck-Cre;Nox4fl/fl, and Mck-Cre;Nox4fl/fl;Gpx1−/− chow-fed (4.8% fat) mice were frozen, and transverse sections were processed for SDH staining and Tomm20 along with dystrophin immunostaining to define mitochondria within individual muscle fibers. (G) Gastrocnemius muscle from 6-month-old male Nox4fl/fl and Mck-Cre;Nox4fl/fl chow-fed (4.8% fat) mice was homogenized. Proteins were digested with trypsin and analyzed on a QExactive HF mass spectrometer. KEGG and differentially regulated proteins were identified considering a P value and log2 fold-change cutoff of ≤0.05 and >|0.3|, respectively. A heatmap of selected differentially expressed proteins associated with OXPHOS is shown. (H and I) Gastrocnemius muscles from 6-month-old male Nox4fl/fl, Mck-Cre;Nox4fl/fl, and Mck-Cre;Nox4fl/fl;Gpx1−/− chow-fed (4.8% fat) mice were processed for (I) qPCR or (J) immunoblotting. (J and K) Twelve-week-old Nox4fl/fl and Mck-Cre;Nox4fl/fl chow-fed male mice were subjected to an acute bout of exercise on multilane treadmill for 50 min at moderate intensity (70% VO2max). After 4 hours, gastrocnemius muscles were excised from sedentary (Sed) and exercised (Ex) mice and processed for (J) qPCR or (K) immunoblotting. Representative and quantified results are shown (means ± SEM) for the indicated number of mice. Significance determined using (A to C and E) a Student’s t test, (H and I) a one-way ANOVA, or (J and K) a two-way ANOVA; # indicates significance using a Student’s t test.