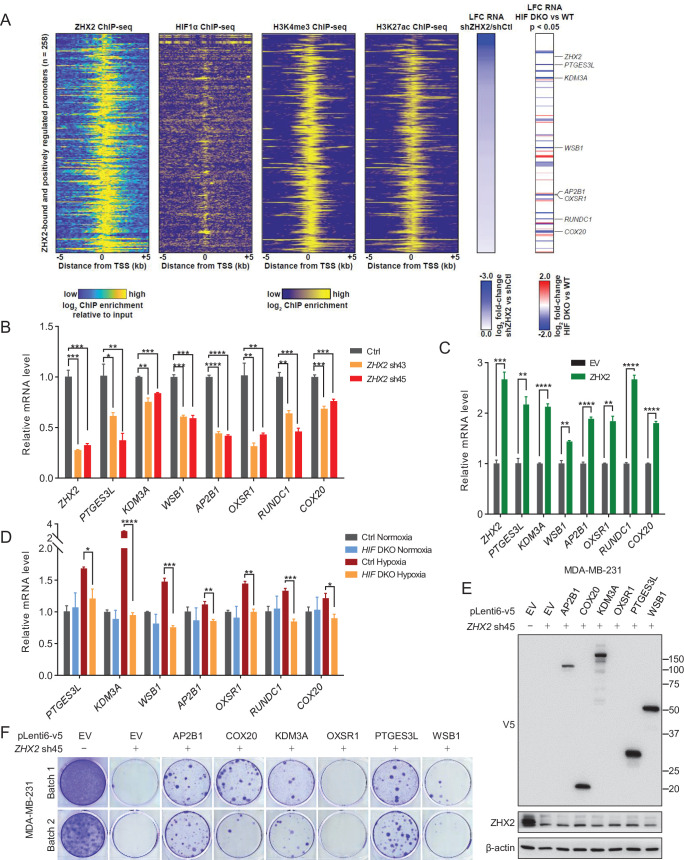
Figure 5. Representative ZHX2 and HIF downstream targets and analysis of their chromatin-binding motifs.
(A) Integrated analyses of ChIP-seqs (including ZHX2, HIF1α, H3K4me3, and H3K27ac), signals expressed as relative to input control when available. Log2 fold change (LFC) for ZHX2 knockdown RNA-seq and HIF double knockout (HIF DKO) RNA-seq; critical target genes were marked on the right. (B–D) qRT-PCR quantification of ZHX2 target genes from MDA-MB-231 cells infected with indicated lentivirus encoding ZHX2 shRNAs (43 and 45) (B), control vector (EV) or ZHX2 (C), or HIF DKO under normoxia (21% O2) or hypoxia (1% O2) (D). (E) Representative immunoblots of cell lysates from MDA-MB-231 cells infected with lentivirus encoding EV or AP2B1, COX20, KDM3A, OXSR1, PTGES3L, and WSB1, and followed by depletion of ZHX2 by sh45. (F) 2D colony formation growth of stable selected cells from (E). Batach1 and 2 indicate two biological experiments. Error bars represent mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM), unpaired t-test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.