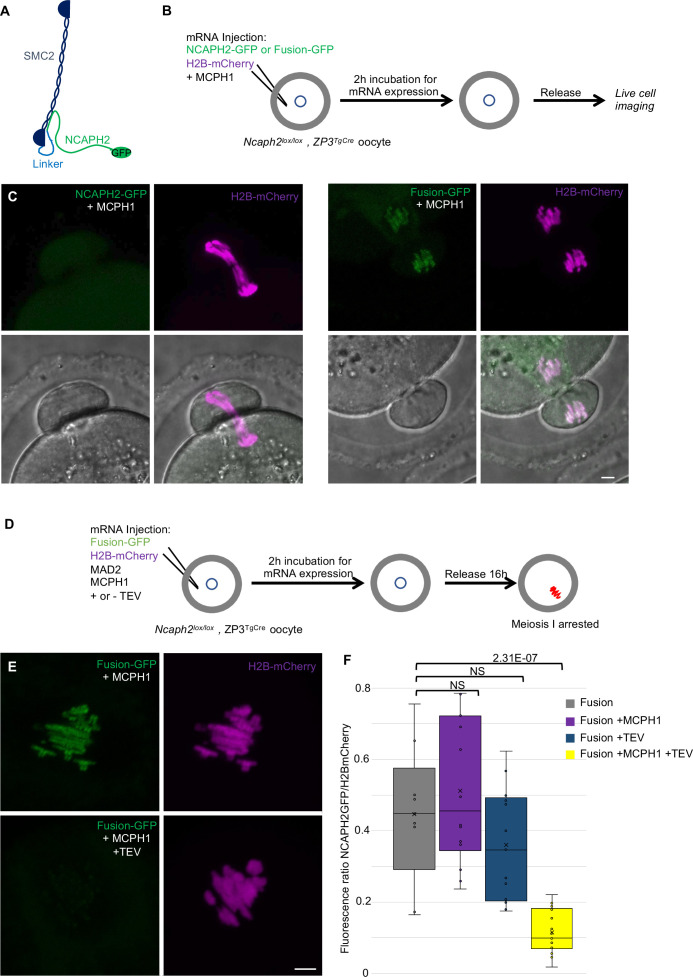
Figure 9. The closure of the SMC2-NCAPH2 interface prevents MCPH1 inhibitory effect.
(A) Schematic representation of the protein fusion between SMC2 C-terminus and the N-terminus of NCAPH2 using a linker comprising three TEV protease cleavage sites. (B) Cartoon summarizing the experimental procedure corresponding to panel C. (C) Oocytes from Ncaph2f/f Tg(Zp3Cre) females were injected at the GV stage with mRNA coding for H2B-mCherry and MCPH1 in combination with NCAPH2-GFP (NCAPH2-GFP+ MCPH1) or with the fusion (Fusion-GFP+ MCPH1). Meiosis I progression was followed by live cell confocal imaging. Maximum intensity z-projections images of the time points corresponding to anaphase I when segregation defects are observed (total number of oocytes showing chromosome segregation defects in three experiments: NCAPH2-GFP+ MCPH1: 17/19, Fusion-GFP+ MCPH1: 0/18). (D) Cartoon summarizing the experimental procedure corresponding to panel E. (E) Oocytes from Ncaph2f/f Tg(Zp3Cre) females were injected at the GV stage with mRNA coding for H2B-mCherry, MAD2 and Fusion-GFP only or in combination with TEV protease. Oocytes were arrested 16 hr after GVBD in metaphase I owing to MAD2 over-expression and maximum-intensity z-projection images of chromosomes were acquired by live cell confocal imaging. (F) Quantification of Fusion-GFP signal on the chromosomes (Total number of oocytes analysed in three experiments: Fusion: 9; Fusion+ MCPH1: 14, Fusion+ TEV: 13, Fusion+ TEV + MCPH1: 18). In each graph the two tailed T-test p values are indicated is indicated. Scale bar, 5 μm.