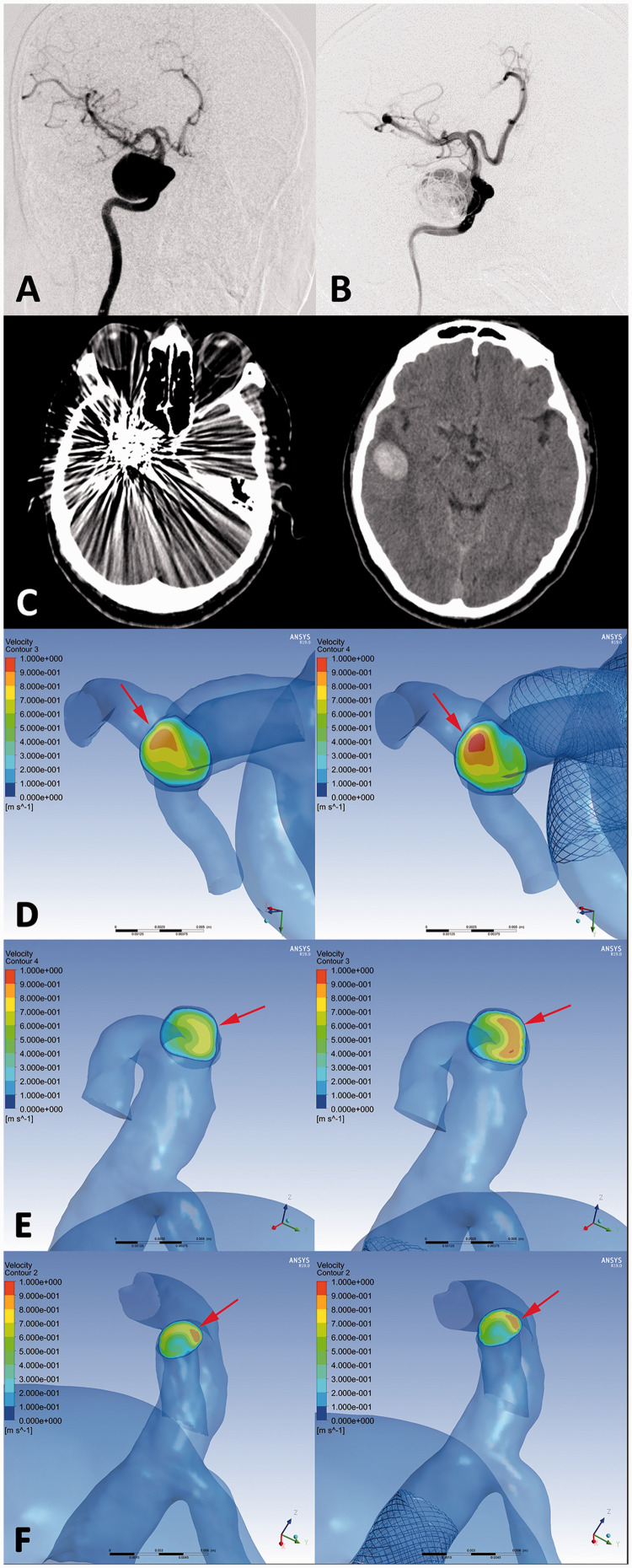
Figure 4.
An ophthalmic segment aneurysm (DIPH 3 in Supplemental Digital Content 1) of right internal carotid artery was treated with the first-generation PED assisted coiling. (a, b) The aneurysm showed residual sac filling at postprocedural immediate angiography(B). CT images showed the coiled aneurysm and DIPH at ipsilateral temporal lobe was found at 2 days later after the procedure (c). In hemodynamic simulation, the velocity on the cross section of terminal internal carotid artery was increased significantly compared with preprocedural results. (Increase rate =10.3%) (d, arrows) Furthermore, the flow velocity of DIPH related artery (middle cerebral artery) have significant increasing after PED treatment (Increase rate =19.6%) (e, arrows), while the velocity of DIPH unrelated artery (anterior cerebral artery) showed no significant change (Increase rate =0.9%) (f, arrows). The imbalance index of distal arteries was 18.7%.