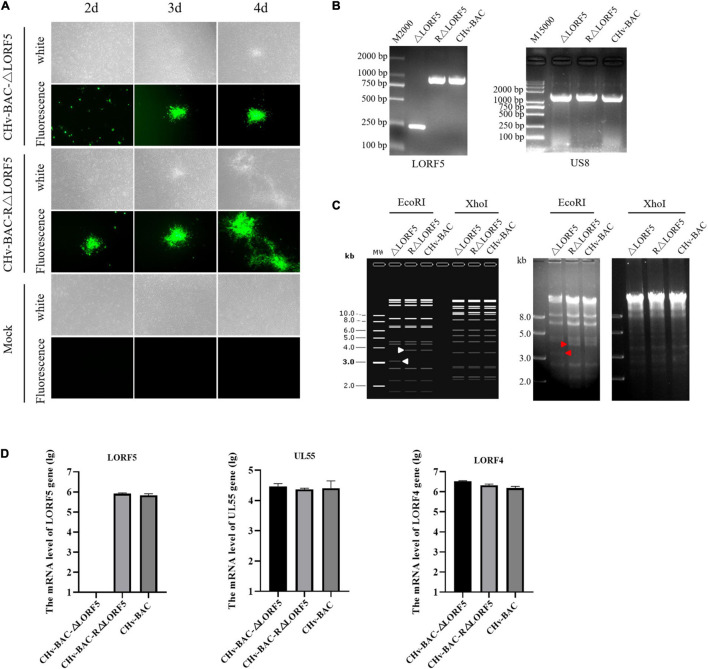
FIGURE 2.
Construction and identification of recombinant viruses. (A) Rescue of the LORF5-deleted mutant and its revertant virus. Plasmids from a positive colony were transfected into DEF cells by Lipofectamine 3000, and with continuous observation, the recombinant virus fluorescent marker protein EGFP was expressed in DEFs. (B) PCR identification of LORF5 gene deletion (245 bp) or restoration (968 bp) using primers ΔLORF5-F and ΔLORF5-R compared with the parental virus DPV CHv-BAC and the US8 gene (1,473 bp) as a DPV gene control. (C) RFLP analysis. The ΔLORF5, RΔLORF5, and BAC plasmids extracted by the Qiagen Plasmid Midi Kit were cut with restriction enzymes EcoRI or XhoI and then imaged by 1% gel electrophoresis; the left is the simulated imaging after restriction digestion. The arrows in the figure show the difference between the deletion strain with WT and the reverting strain after digestion. The corresponding LORF5 gene-deleted strain has a band around 4 kb after EcoRI digestion, and a band around 3 kb has been added. (D) Reverse-transcription q-PCR was performed to verify the mRNA expression of the gene LORF5 and surrounding genes UL55 and LORF4 of the viruses.