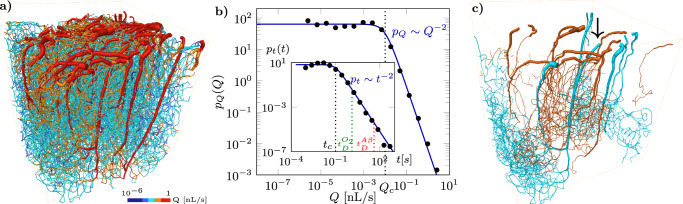
Fig. 1. The blood flow organization in cortical microvessel networks induces broadly distributed flow rates and vessel transit times.
a Simulated blood flow map in a microvascular network feeding 1 mm3 of the mouse cortex (see Supplementary Figure S1a, b and Supplementary Movie S1). Vessel flow rates are represented with blue shades for Q < Qc and red shades for Q > Qc (see also Supplementary Figure S1c, d, f and Supplementary Movie S2). b PDF of simulated flow rates (black dots) compared with the approximation of Eq. (1) (continuous blue line). The characteristic flow rate Qc separating the uniform and power-law regimes are indicated as a dotted line. Inset: PDF of vessel transit times. The diffusion coefficients for oxygen and amyloid-β ( = 2 × 10−9 m2 s−1 and DAβ = 6 × 10−11 m2 s−1) yield diffusion times ( and ) indicated by the green and red dashed lines, respectively. c Example of trajectories visiting <30 vessels (orange) and >70 vessels (blue), originating from the arteriole shown by the arrow (see Supplementary Figure S2a–d and Supplementary Movies S3).