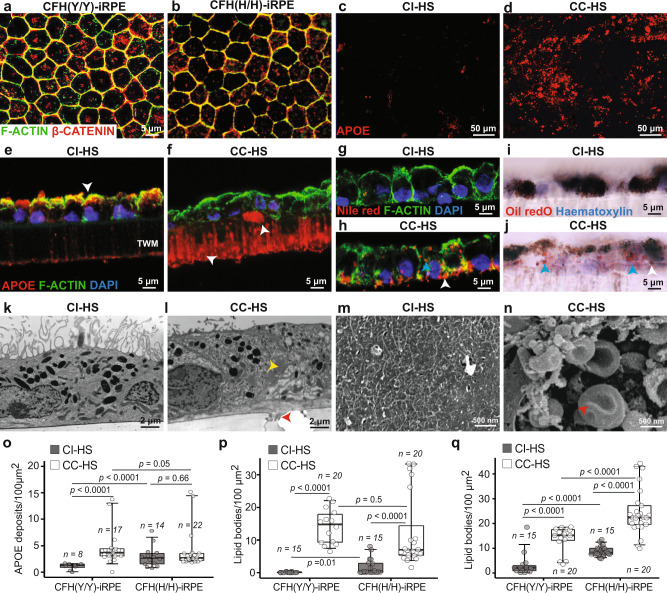
Fig. 1. Complement competent human serum induces AMD cellular phenotypes in mature CFH(Y/Y)-iRPE and CFH(H/H)-iRPE.
a, b Co-localization of F-ACTIN (green) and β-CATENIN (red) at cell borders of mature iRPE cells in CFH(Y/Y)-iRPE1 (a) and CFH(H/H)-iRPE6 (b). (N = 4 biologically independent replicates, iRPE1, 2, 5, 7). c, d APOE-positive deposits in CFH(H/H)-iRPE4 treated for 48 h with complement incompetent human serum (CI-HS) or complement competent human serum (CC-HS) (N = 7 biologically independent replicates, iRPE1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7). e–j Cross-section images of CFH(Y/Y)-iRPE1 monolayer on transwell membrane (TWM) treated with CI-HS (e, g, i) or CC-HS (f, h, j) show changed APOE localization from apical to sub-RPE zone and transwell membrane pores (arrowhead in e, f); intracellular (blue arrowhead) and sub-RPE (white arrowhead) lipid deposits stained with Nile red (h) and Oil Red O (j) (N = 5 biologically independent replicates, iRPE1, 4, 5, 6, 7). k, l Transmission electron micrographs of CFH(Y/Y)-iRPE2 show intracellular lipid droplets (yellow arrowhead) and sub-RPE deposits (red arrowhead) in CC-HS treated (l) cells (N = 5 biologically independent replicates, iRPE2, 4, 5, 8, 9). m, n Scanning electron micrographs of CFH(Y/Y)-iRPE2 sub-RPE surface following CI-HS or CC-HS treatment (red arrowheads show basal deposits in CC-HS treated samples) (N = 3 biologically independent replicates, iRPE2, 5, 8). o–q Quantification of sub-RPE APOE (o), BODIPY (p), Nile red deposits (q) in CFH(Y/Y)-iRPE and CFH(H/H)-iRPE under basal (CI-HS) and CC-HS treatment conditions (N = 7 biologically independent replicates iRPE1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7). P values were determined by multiple pairwise comparisons using two-tailed t test with 95% confidence interval and Bonferroni correction. The horizontal lines in the boxplots indicate the median, the boxes indicate the first and third quartiles, and the whiskers indicate 5th and 95th percentile.