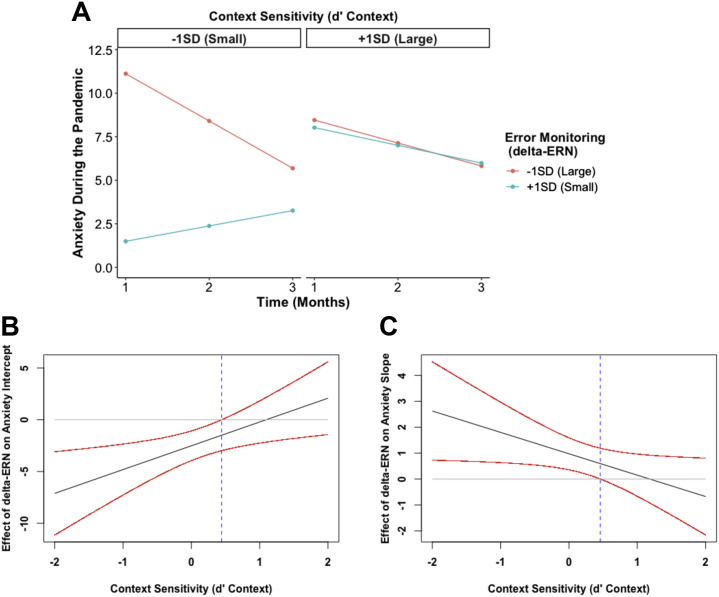
Figure 3.
The impact of error monitoring and cognitive control strategy on anxiety trajectories during the COVID-19 pandemic. More error monitoring (a larger delta-error-related negativity [ERN]) is indicated by a more negative value, and more proactive control is indicated by higher d′ context values. (A) Predicted anxiety trajectories at different levels of error monitoring (delta-ERN) and cognitive control strategy. (B) Johnson-Neyman plot showing that the negative effect of error monitoring on anxiety intercept is greater as children exhibit more a reactive (less proactive) cognitive control strategy. (C) Johnson-Neyman plot showing that the effect of error monitoring on anxiety slope increases as children exhibit more reactive (less proactive) cognitive control.