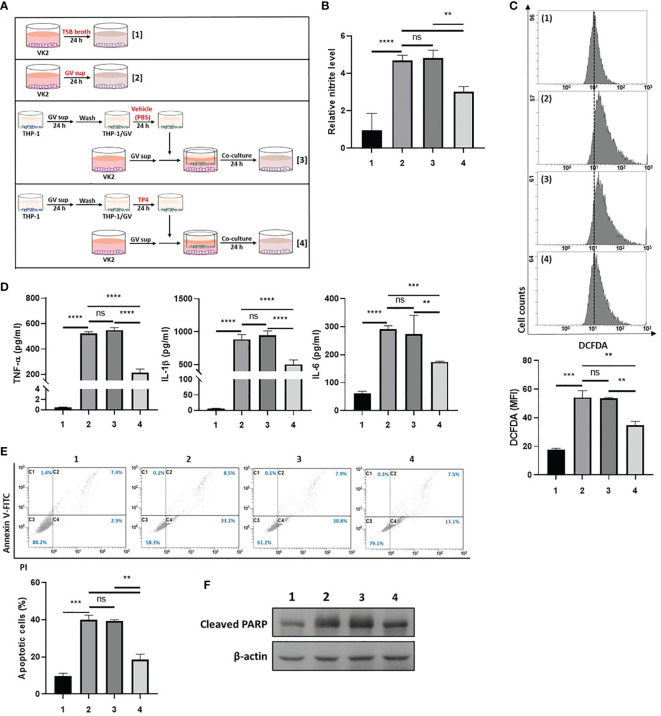
Figure 4.
TP4-induced M2c macrophages attenuate GV sup-induced inflammation and cell death in VK2 cells. (A) Schematic description of the treatment methods. VK2 cells were treated with [treatment 1] TSB broth or [treatment 2] 10% (v/v) GV sup and co-cultured with THP-1/GV cells that had been pre-treated with [treatment 3] vehicle (PBS) or [treatment 4] TP4 (7.82 µg/ml) followed by incubation with serum-free medium. (B) The nitric oxide (NO) levels in VK2 cells were assayed by the NO assay. (C) The reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels in VK2 cells were measured by DCFDA assay using flow cytometry. The mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) is shown in the bar graphs. (D) The secretion of TNF-α (left), IL-1β (middle), and IL-6 (right) by the VK2 cells were measured by MultiPlex assay. (E) The treated cells were double-stained with PI and Annexin V and analyzed by flow cytometry. Four populations were identified: necrotic cells (C1), late apoptotic cells (C2), viable cells (C3), and early apoptotic cells (C4). Apoptotic cell percentage was quantified as the sum of C2 and C4 over total cell number × 100. Data are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments (**P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; ns, not statistically significant). (F) Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage was detected by immunoblotting after co-culture. β-actin was used as an internal control to show equal protein loading.