Fig. 3.
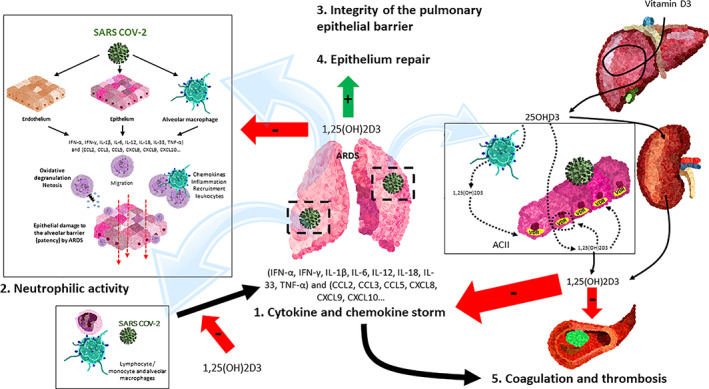
Vitamin D endocrine system and the renin‐angiotensin system. Local or systemic inflammatory reactions may activate the renin‐angiotensin system (RAS) and ACE, thereby generating angiotensin II, which via its receptor (ATR) is able to induce lung damage. During SARS‐CoV‐2 invasion, ACE2 is downregulated in type II alveolar epithelial cells, thereby decreasing the conversion of Ang II to Ang‐(1–7). This prevents the protective action of the Ang‐(1–7) acting on its receptor (Mas R) and all aspects of ARDS. 1,25(OH)2D/VDR is a powerful negative regulator of the RAS, inhibiting renin and the ACE/Ang II/AT1R cascade and inducing ACE2/Ang‐(1–7) axis activity. ACII = cuboidal alveolar type II cells; SARS‐CoV‐2 = severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; Ang I = angiotensin I; Ang II = angiotensin II; Ang‐(1–7) = angiotensin 1–7; MasR = G protein‐coupled Mas receptor; AT1R and AT2R = angiotensin II receptor 1 and 2.
