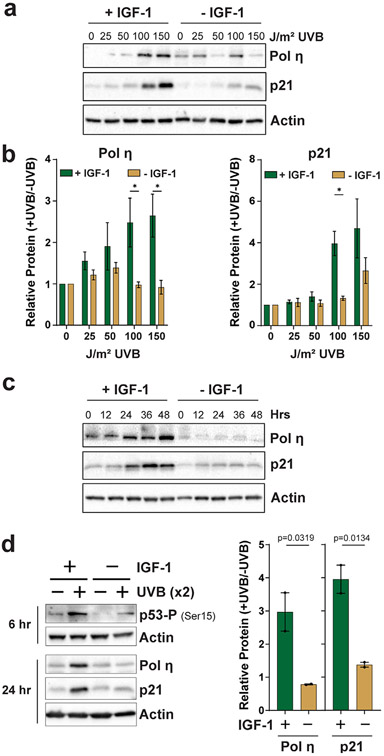
Figure 2.
Characterization of IGF-1 function in pol η and p21 induction in UVB-irradiated keratinocytes. (a) N-TERTs were treated as in Fig. 1 except that cells were exposed to the indicated doses of UVB radiation and harvested 24 h later. (b) Quantitation of protein levels from at least three independent experiments as shown in (a). A multiple t-test analysis was carried out to determine whether the difference between treatment groups was significant at each UVB dose. Asterisks indicate a significant difference (P < 0.05). (c) N-TERTs were cultured in the presence or absence of IGF-1, exposed to 100 J m−2 UVB and then harvested at the indicated time points for protein immunoblotting. (d) N-TERTs were exposed twice (x2) to 100 J m−2 UVB 24 h and 48 h after beginning incubation in medium containing or lacking IGF-1. Cells were harvested 6 h after the second UVB exposure to examine p53 phosphorylation on Ser15 and 24 h after the second UVB exposure to examine pol η and p21 induction. The graphs show the relative level of protein induction from two independent experiments. One-tailed t-tests were used to determine whether the relative protein induction in cells grown with IGF-1 was higher than in the absence of IGF-1.