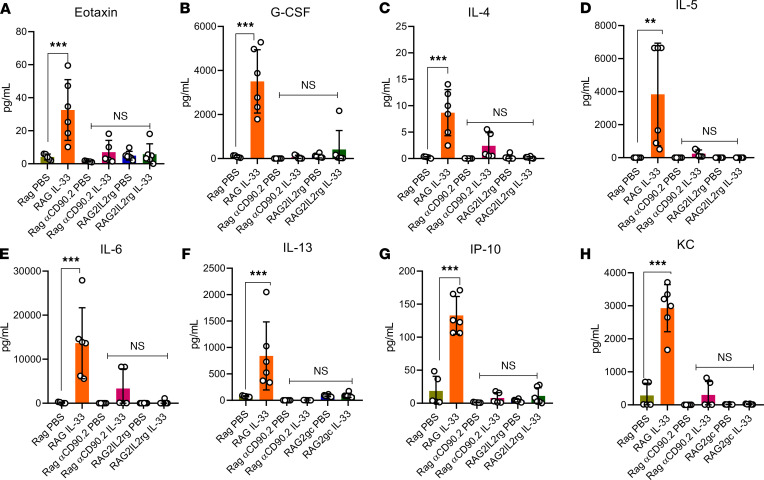
Figure 5. IL-33–driven inflammation is ILC2 dependent.
RAG2–/– mice (ILC2 intact), RAG2–/–αCD90.2 mice (ILC2 depleted), and RAG2–/–IL-2rγ–/– mice (ILC2 deficient) were induced with endometriosis and underwent alternate day i.p. injections of PBS (n = 6) or IL-33 (n = 6). (A) IL-33–treated RAG2–/– mice had significantly elevated levels of eotaxin compared with PBS-treated RAG2–/–, PBS- and IL-33–treated RAG2–/–αCD90.2, and PBS- and IL-33–treated RAG2–/–IL-2rγ–/– mice. (B) IL-33–treated RAG2–/– mice had significantly elevated levels of G-CSF compared with PBS-treated RAG2–/–, PBS- and IL-33–treated RAG2–/–αCD90.2, and PBS- and IL-33–treated RAG2–/–IL-2rγ–/– mice. (C) IL-33–treated RAG2–/– mice had significantly elevated levels of IL-4 compared with PBS-treated RAG2–/–, PBS- and IL-33–treated RAG2–/–αCD90.2, and PBS- and IL-33–treated RAG2–/–IL-2rγ–/– mice. (D) IL-33–treated RAG2–/– mice had significantly elevated levels of IL-5 compared with PBS-treated RAG2–/–, PBS- and IL-33–treated RAG2–/–αCD90.2, and PBS- and IL-33–treated RAG2–/–IL-2rγ–/– mice. (E) IL-33–treated RAG2–/– mice had significantly elevated levels of IL-6 compared with PBS-treated RAG2–/–, PBS- and IL-33–treated RAG2–/–αCD90.2, and PBS- and IL-33–treated RAG2–/–IL-2rγ–/– mice. (F) IL-33–treated RAG2–/– mice had significantly elevated levels of IL-13 compared with PBS-treated RAG2–/–, PBS- and IL-33–treated RAG2–/–αCD90.2, and PBS- and IL-33–treated RAG2–/–IL-2rγ–/– mice. (G) IL-33–treated RAG2–/– mice had significantly elevated levels of IP-10 compared with PBS-treated RAG2–/–, PBS- and IL-33–treated RAG2–/–αCD90.2, and PBS- and IL-33–treated RAG2–/–IL-2rγ–/– mice. (H) IL-33–treated RAG2–/– mice had significantly elevated levels of CXCL1/KC compared with PBS-treated RAG2–/–, PBS- and IL-33–treated RAG2–/–αCD90.2, and PBS- and IL-33–treated RAG2–/–IL-2rγ–/– mice. **P < 0.01, P < 0.0001. Mean ± SD. One-way ANOVA was used.