FIGURE 1.
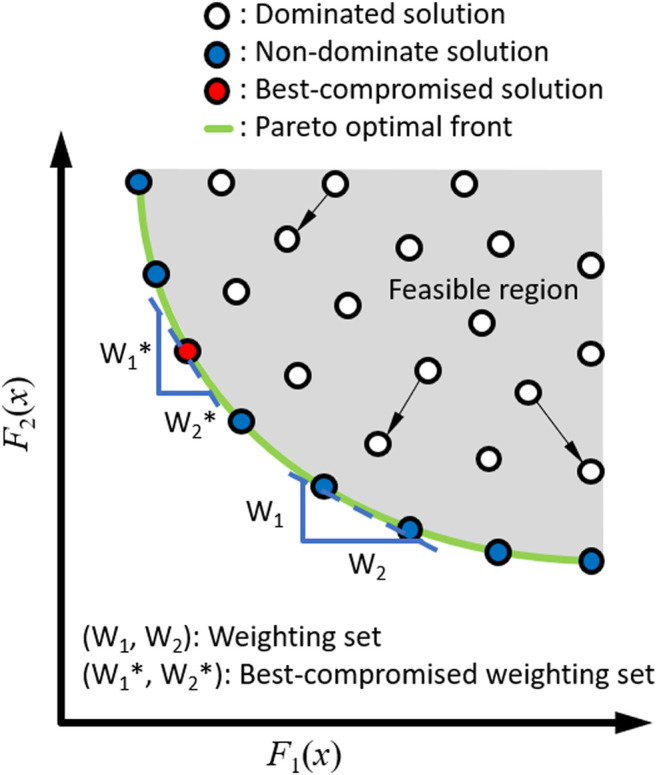
Feasible region, non-dominated (Pareto) solutions (green line) and the best-compromise solution (red circle) of a two-objective optimization problem of a single design variable x in the objective function domain [F 1 (x), F 2 (x)]. Within the feasible region, solutions are called dominated (e.g., white circles) if both objective functions can be improved simultaneously. In contrast, a solution is called non-dominated (filled circles) if none of the objective functions can be improved without degrading the other objective function values. All nondominated solutions are considered equally good unless a single nondominated solution called best-compromise solution is chosen according to the utility function, which defines the decision maker’s preference structure in terms of weightings associated with the objective functions (W1 and W2). The best-compromise weighting set (W1* and W2*) identifies the best-compromise solution that maximizes the decision maker’s utility function among the non-dominated solutions.
