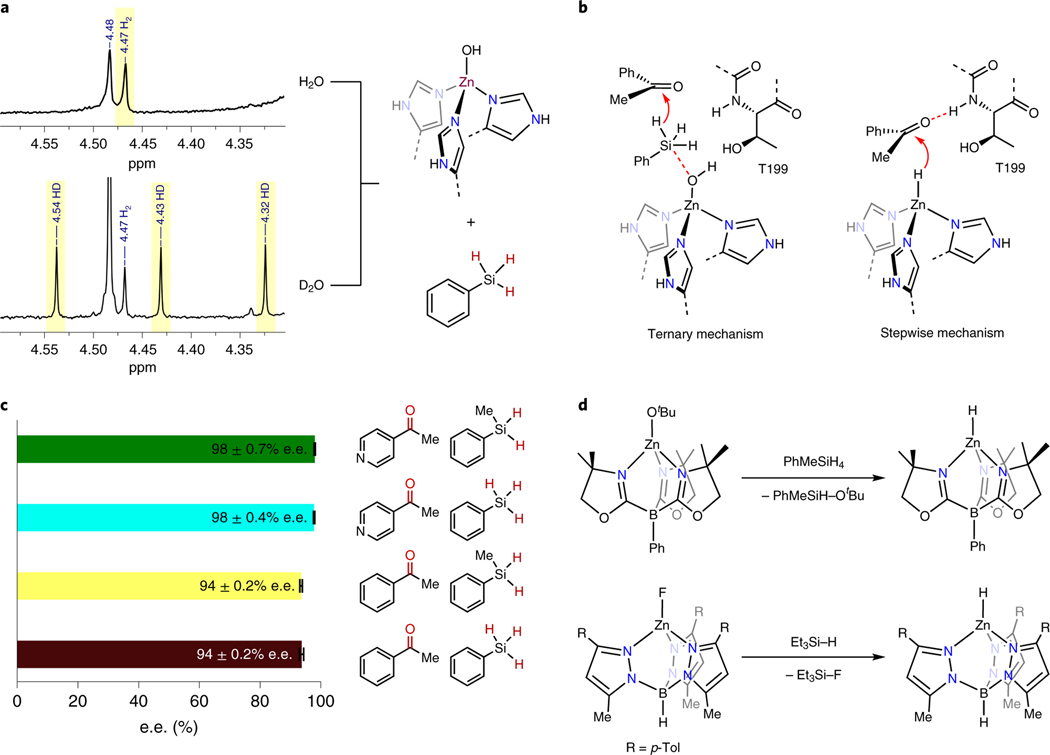
Figure 3. Mechanistic study for the reduction of ketone catalyzed by carbonic anhydrase.
a, 1H NMR spectra of H2 and HD generated by reaction of hCAII with phenylsilane in H2O and D2O. The NMR signal at 4.48 ppm is residual PhSiH3. b, Two potential mechanisms for reduction of the ketone with PhSiH3, including a ternary mechanism (left) and a stepwise mechanism (right). c, hCAII-catalyzed reduction of 4-acetylpyridine (green and cyan) and acetophenone (yellow and brown) by different silanes. Data are presented as average values and error bars are calculated as the standard deviation. n=3 independent experiments, individual data points are shown as gray circles. d, Formation of zinc hydride from the reaction of zinc alkoxide (top) and zinc fluoride (bottom) with silanes.