FIGURE 3.
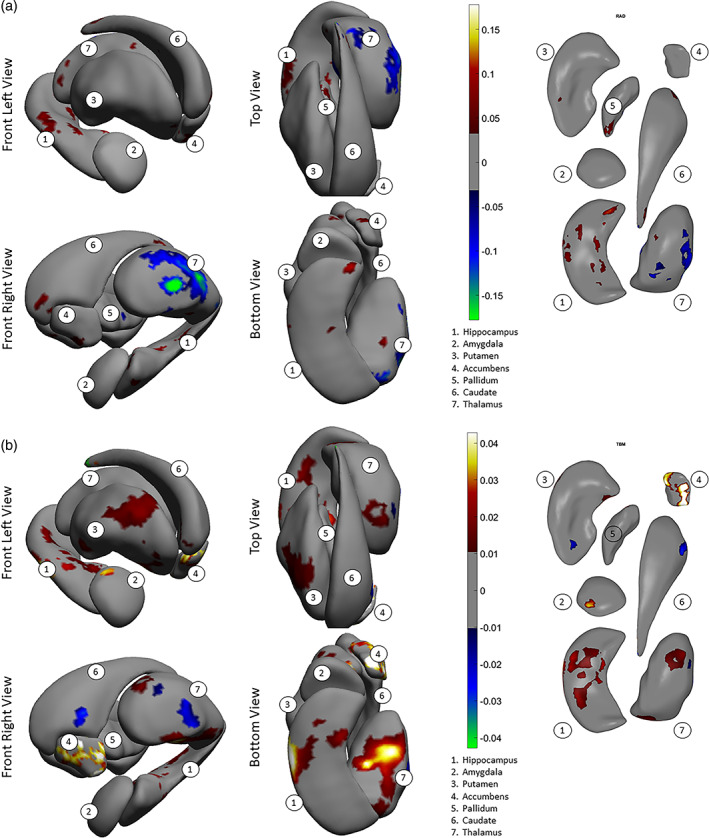
Effects of diagnosis (i.e., schizophrenia vs. control) for (a) asymmetry index of thickness, (b) asymmetry index of surface dilation/contraction (log Jacobian determinant). Vertex‐wise asymmetry indices for thickness and surface dilation/contraction were calculated as the absolute values of left‐versus‐right differences. The effects are tested in models that included diagnosis sex, age, age x sex, age2, age2 x sex, and ICV. Effect sizes (Cohen's d, see text) are visualized on subcortical surfaces. In the left two columns, the subcortical structures—1. hippocampus, 2. amygdala, 3. putamen, 4. accumbens, 5. pallidum, 6. caudate, and 7. thalamus—are shown as a group situated in template space, from front left, front right, top and bottom viewpoints of the brain. L = left hemisphere. R = right hemisphere. In the right column, the subcortical structures are positioned generally from a bottom viewpoint, with some slightly rotated about their own principal axis to be oblique, for better exposure: caudate—pi/7 or about 25°, accumbens—pi/10 or 18°, pallidum—pi/3 or 60°. Color scale indicates intensity of effect sizes. Cooler colors (i.e., negative effect sizes) indicate reduced asymmetry for schizophrenia as compared with controls, and warmer colors (i.e., positive effect sizes) indicate exaggerated asymmetry. Gray color indicates nonsignificant surface vertices after multiple comparison correction
