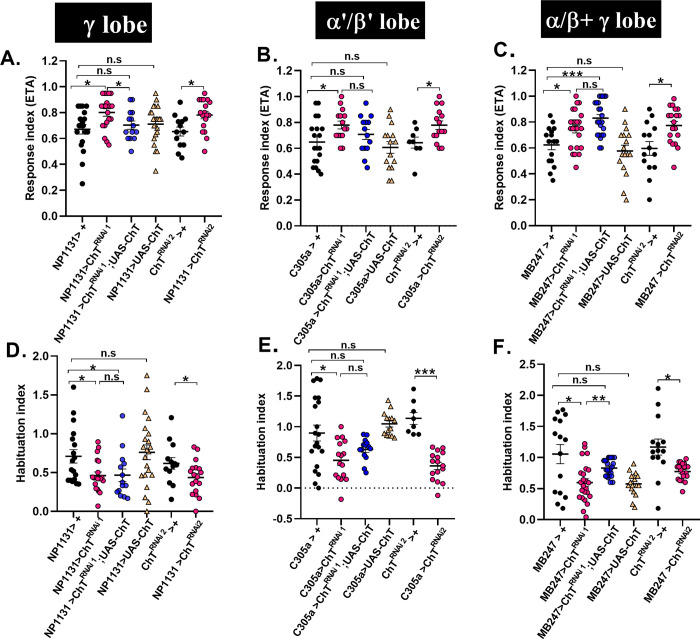
Fig 2. Knock-down of ChT in MB intrinsic neurons enhances chemotaxis towards odour but suppresses habituation.
(A-C) Response index of naïve larvae (also referred to as chemotaxis) towards ETA, (D-E) habituation index of larvae exposed to ETA, of genotypes: NP1131GAL4 was used as a driver line for expression in MB γ-lobe. Scatter plot represents R.I (A) and H.I (D) of genotypes NP1131> UAS-ChTRNAi1, NP1131>UAS-ChTRNAi1;UAS-ChT, NP1131> UAS-ChT as compared to their controls NP1131> +. NP1131> UAS-ChTRNAi2 as compared to UAS-ChTRNAi2>+. C305aGAL4 was used as a driver line for expression in MB α’/β’-lobe. Scatter plot represents R.I (B) and H.I (E) of genotypes C305a> UAS-ChTRNAi1, C305a> UAS-ChTRNAi1;UAS-ChT, C305a> UAS-ChT as compared to their controls C305a> +. C305a> UAS-ChTRNAi2 as compared to ChTRNAi2>+. MB247GAL4 was used as a driver line for expression in MB α/β+ γ lobe. Scatter plot represents R.I (C) and H.I (F) of genotypes MB247> UAS-ChTRNAi1, MB247> UAS-ChTRNAi1;UAS-ChT, MB247> UAS-ChT as compared to their controls MB247> +. MB247> UAS-ChTRNAi2 as compared to UAS-ChTRNAi2>+. Pink circles represent knockdown using UAS-ChTRNAi1 and UAS-ChTRNAi2, Blue circles represent rescue, and yellow triangles represent transgenic over-expression of UAS-ChT as compared to genetic controls (black circles). Data are represented as scatter plot with error bars showing SEM and N≥16. Each N represent one experiment performed with a group of 40 larvae. Each data group was analysed for normal distribution using Shapiro-Wilk test. Statistical significance was determined by two-tailed unpaired t-test (parametric) with Welchs correction. *** represent p≤0.0001, n.s means statistical non-significance when p≥0.05. For more statistical details and numerical data values in the scatter plot refer to S1 and S2 Data.